Recently, the group of Prof. WANG Wencheng and HOU Fei from the Institute of Software of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a new topology-preserving simplification method for Medial Axes in 3D models. Compared with existing methods, the proposed method has advantages in the geometric approximation accuracy and efficiency, while preserving the topology.
The Medial Axis is an important descriptor of geometry and topology of a 3D model. It has many applications in shape analysis and manipulations. However, the instability to noises of the medial axes makes it necessary to simplify the medial axes for further usage. Existing methods have different kinds of drawbacks. Some lack geometric approximation accuracy and some cannot preserve the topology, while some of the others are time-consuming due to topology-check (Fig. 1).
The group summarized a novel and simple topology-check strategy for identifying the edges whose collapses could change the topology. With the strategy, the new method can skip the contraction of those edges during the simplification, and thus preserve the topology.
Meanwhile, they proposed to restrict the topology-check in the areas near the holes to avoid much unnecessary topology-check (Fig. 2). Besides, in order to accelerate the whole method, they proposed a parallel framework for edge-contraction based simplification. The new method is not only as accurate as the geometric approximation of edge-contraction methods but also much more efficient to preserve the topology.
The research is not only meaningful for the shape understanding and analysis, but also contributes a lot to the wide application of medial axes in other fields.
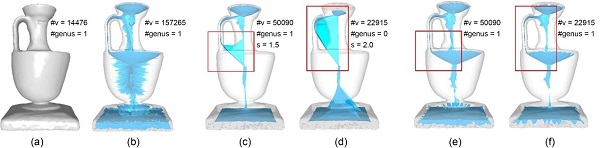
Fig. 1. Simplifications of the medial axis of the vase. (a) Original vase model. (b) Initial medial axis. (c)-(d) Simplified medial axes using the SAT method [MGP10] by different scaling parameters s. (e)-(f) Results using our method at correspondingly similar levels of simplification. (Image by HOU Fei)
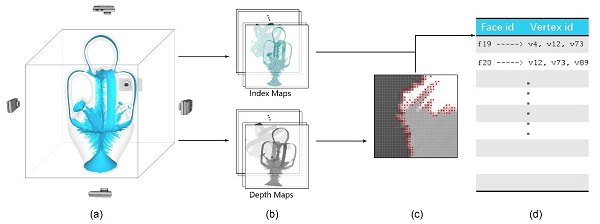
Fig. 2. The process of extracting critical areas, where edge-collapse potentially changes the topology. (Image by HOU Fei)






