
A research team led by Prof. FANG Yonghua from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a Raman spectroscopy gas detection system based on a double-cycle circular confocal cavity (C-CERS), offering a practical solution for detecting trace gas.
The results were published in Optics Letters.
Raman spectroscopy offers unique fingerprint identification, but its signals are inherently weak. Although optical cavity techniques can amplify these signals, conventional methods are often susceptible to environmental disturbances or require intricate optical alignment, which limits their reliability and practical application.
To address these challenges, the researchers designed a circular, multi-pass cavity composed of multiple spherical mirrors arranged so that their focal points converge at the center of the ring. This confocal structure gives the system high tolerance to misalignment, allowing the laser beam to remain stably confined even under lateral or longitudinal offsets or when the beam has a large divergence angle. This design ensures excellent stability in complex field environments.
The researchers further enhanced detection sensitivity by introducing a retro-reflector to create a double-cycle configuration, in which the laser traverses the cavity twice: first in the forward direction and then back along its original path. This approach effectively doubles the optical path length and recycles backward-scattered signals that would otherwise be lost. Experimental tests confirmed that this configuration significantly enhances Raman signal strength and overall detection performance.
Using this system, the researchers successfully detected trace gases in air under normal conditions, including carbon dioxide, water vapor, and oxygen isotopes, demonstrating both high sensitivity and robust performance.
"Our work tackles a major challenge in cavity-based Raman systems: their extreme sensitivity to alignment," said LI Zhengang, a member of the team.
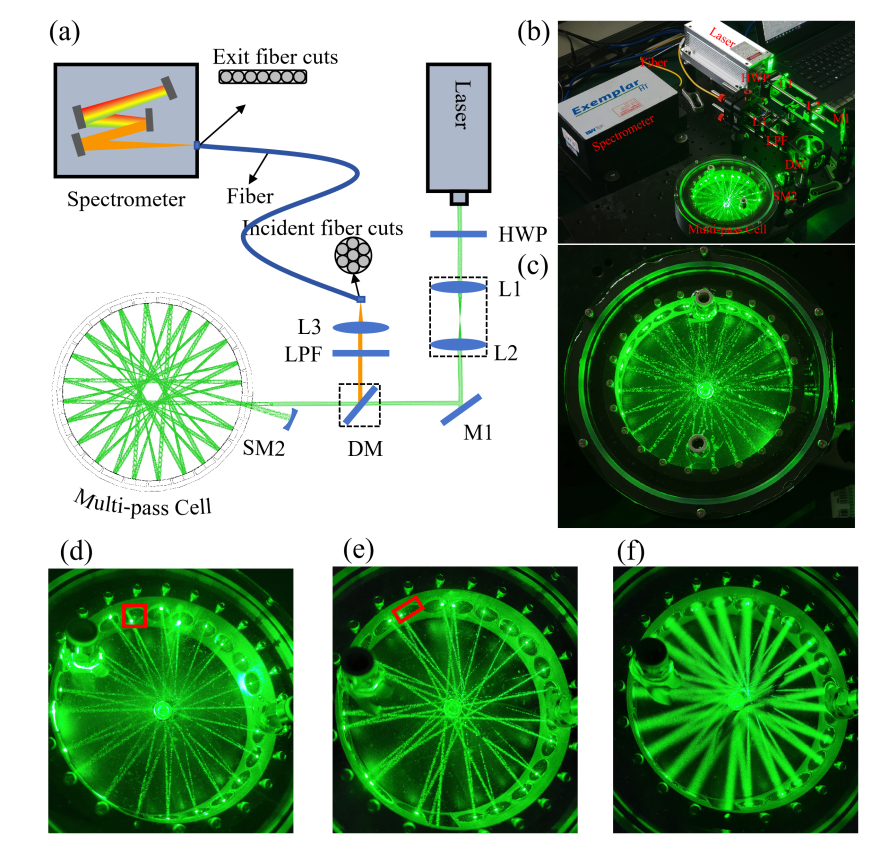
Schematic of the C-CERS system and experimental results of beam offset (Image by LI Zhengang)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

