
Ferroelectric tunnel junction (FTJ) is a junction in which a thin ferroelectric film is sandwiched between two metal electrodes. The resistance is highly dependent on the polarization direction of the ferroelectric barrier. Two greatly different states with high and low resistances respectively can be obtained by reversing the polarization direction with an external electrical field.
FTJ plays an important role in non-volatile random access memory.
In a recent study published on Physical Review Applied, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have investigated the interface control of transport properties of perovskite oxide FTJs, and a new scheme to realize giant tunneling resistance (TER) in FTJs has been proposed.
According to ZHENG Xiaohong, who led the team, TER ratio up to 105 % was obtained by introducing a negative polar atomic layer at one of the interfaces of the symmetric Pt/BaTiO3/Pt FTJ.
In the symmetric Pt/BaTiO3/Pt FTJ, a negative NaO2 or LiO2 interface was formed by replacing Ti with Na or Li atoms at the right interface of Pt/BaTiO3/Pt tunnel junction. Then the TER ratio was achieved due to this additional NaO2 or LiO2 layer.
The mechanism is rooted in the great difference in the potential change in the ferroelectric barrier arising from the negative polar interface of the two polarized states.
When the ferroelectric barrier is left polarized, the bands of the barrier at each atomic layer increase from left to right. Meanwhile, due to Coulomb repulsion, the negatively charged NaO2 or LiO2 interface further pushes up the bands of the barrier. Near the right interface region, the valence band maximum (VBM) rises above the Fermi energy, resulting in partial metallization.
On the contrary, in the right polarization state, although the Coulomb repulsion at the NaO2 or LiO2 interface still exists, the band of the ferroelectric barrier itself decreases from left to right. Due to the cancellation between them, the valence band distribution in the whole barrier is relatively flat and the VBM is always below the Fermi energy, without the occurrence of partial metallization.
The occurrence and disappearance of partial metallization in the two polarization states change the effective barrier width significantly and lead to the low and high resistance states, with a giant TER ratio achieved subsequently.
The study indicates that a negatively charged polar interface based on interfacial substitution is a feasible scheme to achieve large TER ratio in FTJs, which provides important reference for the design of high-performance FTJs.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and all calculations were performed at the Center for Computational Science of CASHIPS, the ScGrid of Supercomputing Center and the Computer Network Information Center of CAS.
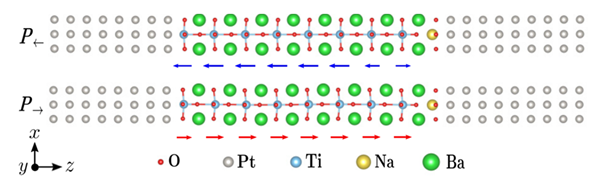
Figure 1. The schematic diagrams of the atomic structures in the left and right polarization states of NaTi-FTJ. (Image by XIAO Wei)
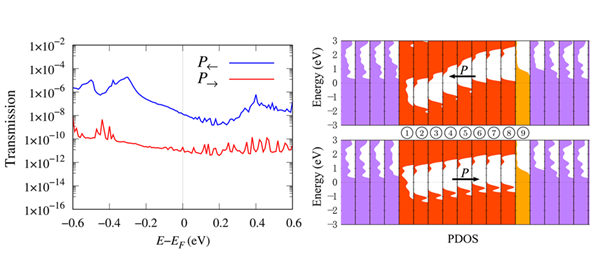
Figure 2. The k-averaged transmission and layer-resolved density of states of two polarization states of NaTi-FTJ. (Image by XIAO Wei)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

