
Recently, Prof. ZHENG Xiaohong's research group from the Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP) of the Hefei Institute of Physical Science (HFIPS) predicted a new two-dimensional (2D) tin dioxide (SnO2) monolayer phase (P-4m2) via first-principles calculations.
Bulk SnO2 is an important n-type wide-bandgap (~3.6 eV) semiconductor and is widely used as electrode materials, chemical sensor components, etc. but systematic study of possible tin oxide phases in 2D is still missing. In particular, given the claims of magnetism in SnO2 thin films, it is worth investigating whether a stable SnO2 2D phase can be synthesized or magnetism can be induced.
In this research, the researchers provided direct evidence of a stable and new 2D phase of SnO2 (δ- SnO2) with auxetic properties based on density functional theory method, which was impressive for its negative in-plane Poisson's ratio and high electron mobility.
In addition, they found double Mexican-hat-like band edges near the Fermi level presented by the valence band structure of SnO2 and therefore a ferromagnetic phase transition and half-metallic ground state could be induced by hole doping within a very wide concentration range.
They also proved that SnO2 monolayer could be tuned to be either an XY magnet or an Ising one, with a magnetic critical temperature above room temperature at proper hole concentrations.
All the above findings indicated that the predicted 2D phase of SnO2 provided a new example of rare p-type magnetism and a potential candidate material for spintronic applications.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the China Scholarship Council.
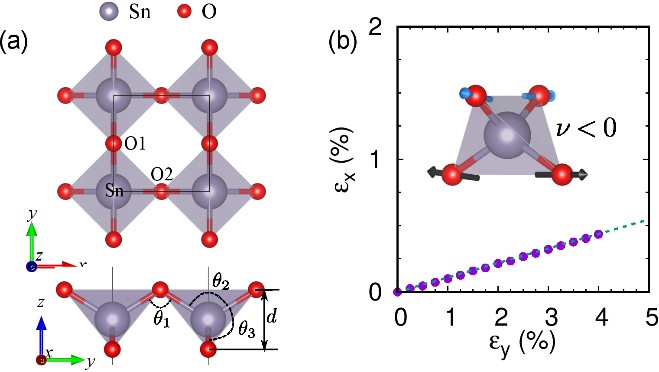
Fig. 1. (a) The atomic structure of a 2D δ-SnO2 monolayer. (b) The strain in the x direction resulting from an applied tensile strain in the y direction. (Image by JIANG Peng)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

