
A research team led by Prof. WANG Haoyi from the Institute of Zoology (IOZ) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cell exhaustion model and a functional screening platform for identifying compounds that can rejuvenate exhausted T cells. Using this innovative platform, the team identified the small-molecule compound miltefosine, which significantly enhances the tumor-killing activity of CAR-T cells. This study was published in Cell Reports Medicine on December 9.
T cell exhaustion is a differentiation state that arises when T cells are exposed to persistent antigen stimulation. This state is characterized by a progressive loss of effector functions, sustained expression of inhibitory receptors, impaired proliferation, and compromised mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis capacity.
T cell exhaustion is a critical obstacle to the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) and CAR-T cell immunotherapies. Manipulating the exhaustion process may improve the therapeutic efficacy of T cell responses in cancer.
To address this problem, the researchers generated hypofunctional CAR-T cells through multiple rounds of tumor challenge and established a drug screening platform using these cells. By screening FDA-approved drugs, they discovered that miltefosine——a small molecule previously used to treat leishmaniasis——could restore the functionality of exhausted CAR-T cells. Remarkably, even in a terminally exhausted state where PD-1 antibody therapy proved ineffective, miltefosine was still capable of boosting CAR-T cell activity.
Through single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis, the researchers discovered that miltefosine enhances effector function, reduces exhaustion, and improves metabolic activity in hypofunctional CAR-T cells. Further investigations revealed that miltefosine rescues the glucose uptake deficit and improves glycolytic and oxidative phosphorylation metabolism in a GLUT1-dependent manner. These effects ultimately lead to improved efficacy in treating solid tumors.
Moreover, in both allogeneic and syngeneic tumor models, miltefosine significantly enhanced the tumor-clearing capacity of CAR-T cells and T cells.
The drug screening platform can assess FDA-approved small molecules using the CAR-T cell exhaustion model. Miltefosine has emerged as a promising candidate for improving CAR-T cell function and metabolic activity, demonstrating potential for application in immunotherapy.
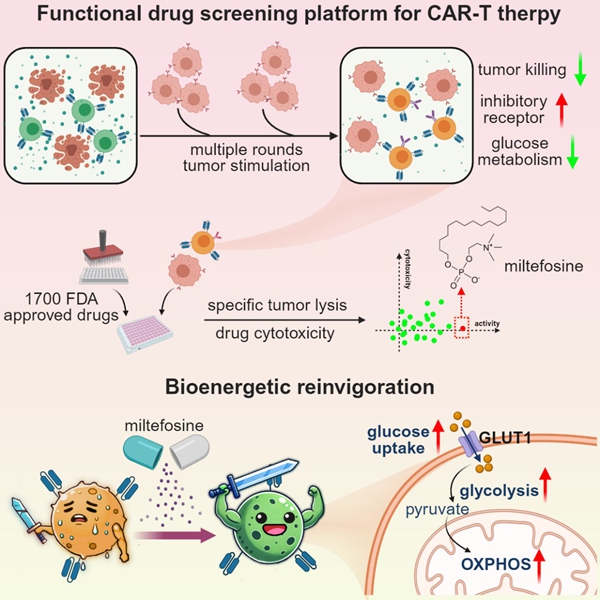
Diagram of the drug screening platform and the mechanism of miltefosine in CAR-T cells (Image by Prof. WANG's group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

