
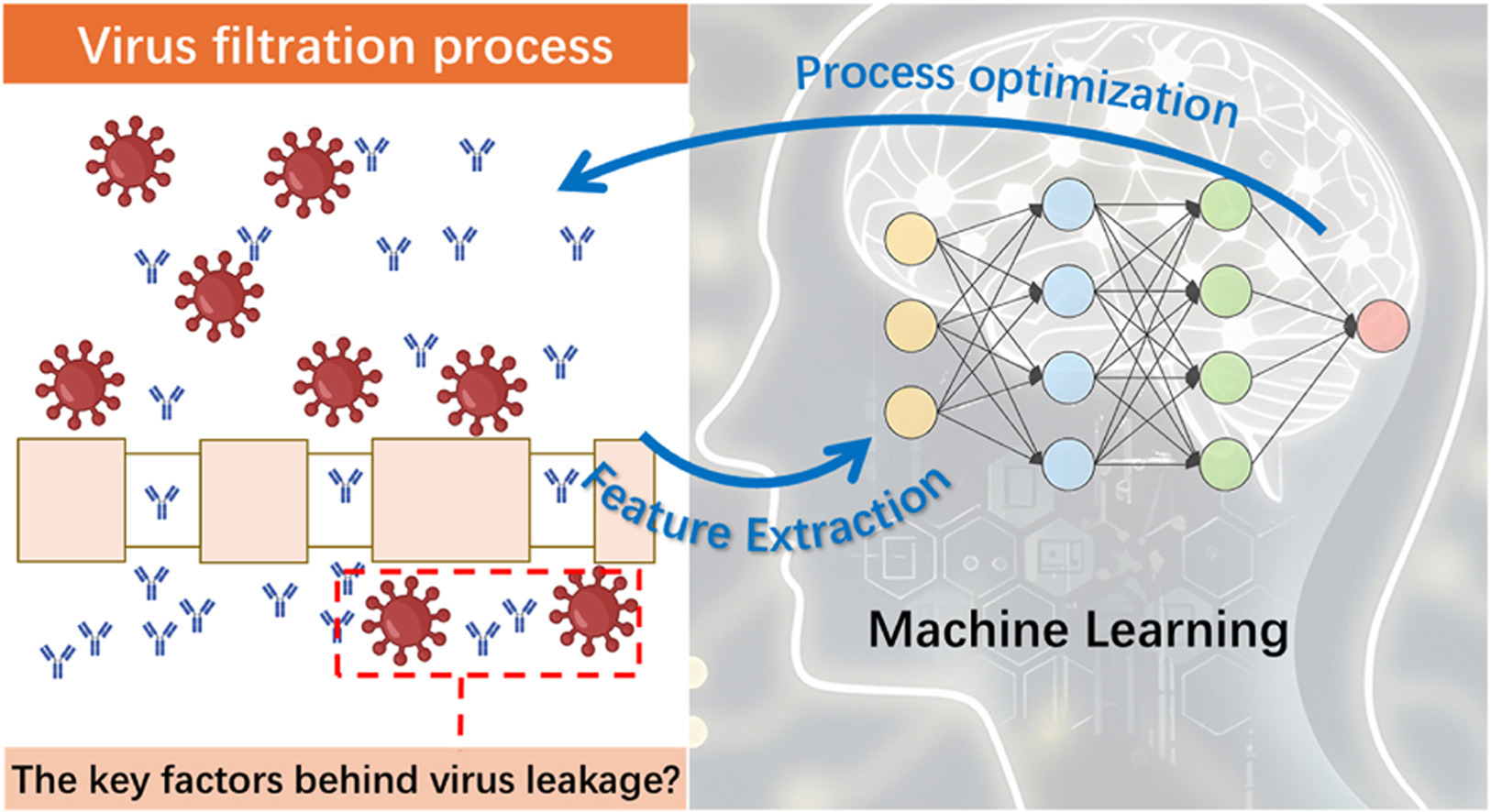
A research team led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering has developed a machine learning framework to analysis virus filtration processes in therapeutic protein purification. The new method enables intelligent identification of critical parameters affecting virus retention efficiency and provides predictive guidance for process optimization.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Shuqiang from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a Prior-Guided Adversarial Learning with Hypergraph (PALH) model for predicting abnormal connections in Alzheimer's disease.
Researchers from the Hefei Institute of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have identified a key molecular module that regulates rice plant architecture, providing valuable genetic resources and regulatory modules for molecular breeding.
Researchers from the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have conducted a new study on the temporal evolution of the afterglow from gamma-ray burst GRB 240825A. The study offers new evidence to better understand the physical environment surrounding gamma-ray bursts and provides insights into the mechanisms that govern their afterglow emission.

A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science has introduced a soil amendment called humic acid-modified bentonite. This amendment effectively enhances a soil's ability to hold onto ammonium while significantly reducing harmful nitrogen losses.
Researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with international partners, have engineered a thin two-dimensional perovskite phase at the buried interface of three-dimensional perovskite solar cells (PSCs) to boost device performance and operational stability.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Hongzhi and Prof. HONG Bo from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. WANG Wei from the First Affiliated Hospital of the University of Science and Technology of China, discovered a crucial mechanism that underlies chemotherapy resistance and metastasis in small cell lung cancer.
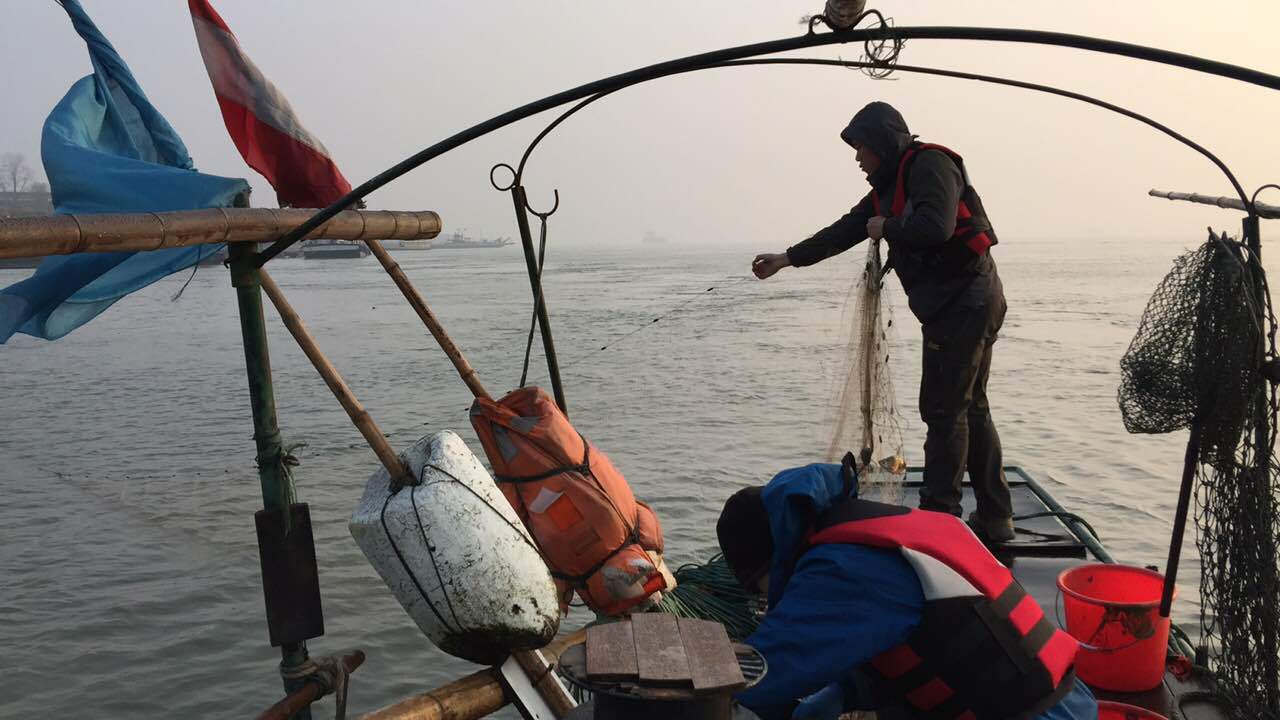

Researchers led by Prof. CHEN Yushun from the Institute of Hydrobiology (IHB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with domestic and international collaborators, have revealed that the Yangtze River fishing ban has not only halted the 70-year decline in fish resources but has also triggered an initial recovery.
In a new review, researchers from the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography synthesized evidence and proposed a multi-objective optimization framework for designing farmland windbreak systems that can better sustain agriculture in arid regions.

Researchers from the Institute of Subtropical Agriculture conducted a series of investigations to assess the cycling processes of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, as well as the community properties, functions, and interaction patterns of belowground biota in karst farmland regions of Southwest China.
Researchers from the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, have developed a high-resolution daily atmospheric carbon dioxide dataset covering China from 2016 to 2020.
A research team led by Prof. LI Xiangxian from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a new deep learning model that significantly enhances both the accuracy and interpretability of roadside air pollutant forecasts.

A research team led by Prof. FANG Yonghua from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science proposed and systematically optimized a novel parabolic mirror cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy technique, achieving a marked improvement in gas detection sensitivity through the integration of advanced optical design and signal processing methods.
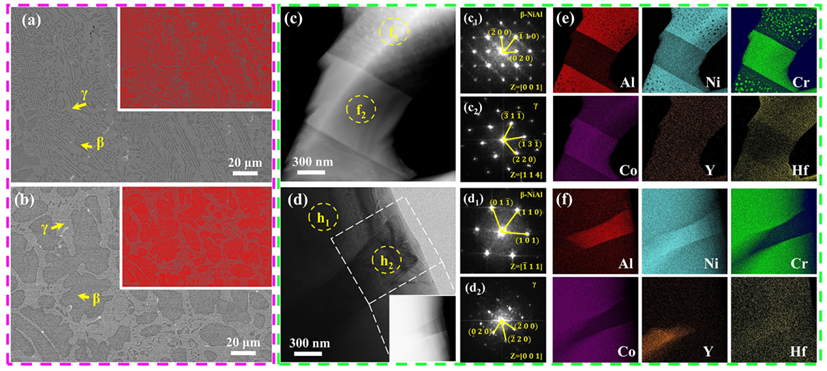
A research team from the Institute of Metal Research has developed a novel bond coat material that significantly enhances the oxidation resistance of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) at 1,200 °C, a critical advancement for next-generation ultra-high-thrust aero-engines.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

