
90Sr is one of the main hazardous elements in nuclear waste with strong radioactivity and high heat release, Ba is a simulant for 226Ra due to their similar ion exchange behaviors, and [UO2]2+ ions with high water solubility can easily enter the food chain with serious health effects. Therefore, it is of great significance to capture these ions for environmental protection.
Cluster-based functional materials have been reported in the field of removing radioactive ions, however, it is mainly focused on polyoxometalates (POMs) such as polyoxomolybdates. Other types of cluster-based compounds for removal of radioactive ions still need to be explored.
In a recent study published in ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., Prof. FENG Meiling from Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter (FJIRSM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, reported the first Sb-oxo-cluster-based material, namely (H3O)7[Cd7Sb24O24(L-tta)9(L-Htta)3(H2O)6]·29H2O (FJSM-CA), for capturing Sr2+, Ba2+, and [UO2]2+ ions from aqueous solutions.
FJSM-CA is the first case of organic-inorganic hybrid compounds based on the cadmium-antimony oxo-cluster. It contains two types of bowl-shaped anion clusters, namely, {[Cd4Sb24O24(L-tta)9](L-Htta)3}13- and {(L-Htta)3[Cd4Sb24O24(L-tta)9]Cd3(H2O)6}7-, which are the largest hybrid Sb-oxo-cluster units so far.
{[Cd4Sb24O24(L-tta)9](L-Htta)3}13- and {(L-Htta)3[Cd4Sb24O24(L-tta)9]Cd3(H2O)6}7- are connected by [CdO4(H2O)2] units to form a two-dimensional honeycomb anionic layer of [Cd7Sb24O24(L-tta)9(L-Htta)3(H2O)6]n7n-. [H3O]+ as counter cations are filled in between the anion layers. Stability studies showed that FJSM-CA has excellent water/solvent- and acid/alkali-resistances and radiation stabilities.
The advantages of FJSM-CA as ion-exchange material include rapid kinetics, high exchange capacity and high selectivity. FJSM-CA exhibits fast adsorption abilities with short equilibrium times for Sr2+ (2 min), Ba2+ (10 min), and [UO2]2+ (20 min). It has high adsorption capacity for uranium (qmU = 121.91 mg/g) than those of a series of MOFs including SZ-2/SZ-3 (58.18 mg/g), UiO-66 (109.9 mg/g), and MIL-101-NH2 (90 mg/g). It also shows high removal rate R (96%) and distribution coefficient KdU (2.46 × 104 mL/g) for uranium in the presence of Sr2 and Ba2+ ions.
The researchers revealed the ion-exchange mechanisms at the atomic level by single-crystal structural analyses, which is attributed to strong electrostatic interactions between the highly negative-charged layers and exchanged cations, and the strong coordination effect of the carboxyl functional group on Sr2+, Ba2+ and [UO2]2+ ions.
Besides, structural transformations occur after ion-exchange, that is, the two-dimensional structure of FJSM-CA is changed to three-dimensional ones of FJSM-CA-Sr, FJSM-CA-Ba and FJSM-CA-UO2.
This study not only presents the first case of removal of radionuclides by Sb-oxo-cluster-based materials, but also provides an important research foundation for the deep understanding of the relationship between structure and property.
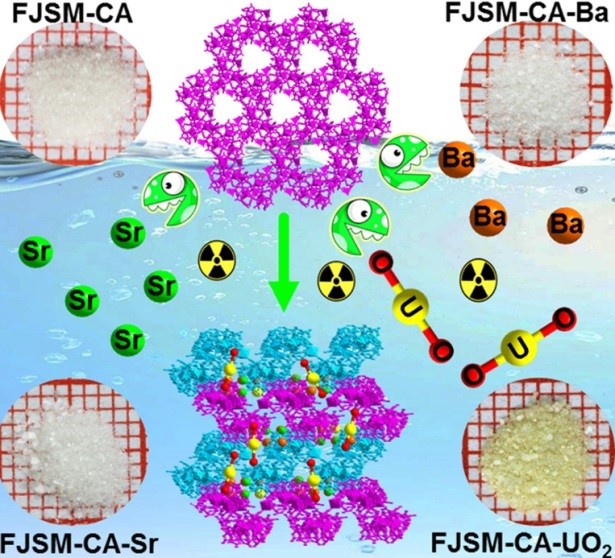
The uptake of Sr2+, Ba2+ and [UO2]2+ ions into a Sb-oxo-cluster-based material with structural transformation (Image by Prof. FENG Meiling)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

