
Optical smoothing is a very effective method to restrict mid-to-high spatial frequency errors generated by computer controlled sub-aperture polishing technologies. According to Preston equation, pressure distribution is the key factor to describe the smoothing effect of a tool.
Though the classic bridging model can solve pressure distribution during smoothing process, it is only suitable for a tool of rigid base, compliant interlayer, thin metal plate and pitch polishing layer.
Recently, a research group from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences established a mathematical model to calculate the pressure distributions between a polishing tool and a mirror for any kind of multi-layer polishing tool. The related results were published in Applied Optics.
Based on Galerkin's displacement functions, the compression, bending and shearing deformation were all taken into consideration.
In their experiment, the displacement and stress continuous conditions between layers were processed by using Cauchy equation and Hooke's law. The researchers employed a rigid tool and a semi-flexible tool as two examples and theoretically compared in details for their applications in optical smoothing.
In this way, they verified validity and improvement in accuracy of the pressure distribution model by comparing with the finite element model (FEM).
Based on the pressure distribution model, the total stiffness of a tool was deduced. The theoretical comparison smoothing effects for different polishing tools were carried out by calculating the ratio of their total stiffnesses.
Moreover, they carried out three groups of experiments by using a rigid tool and a semi-flexible tool for smoothing 4mm and 8mm period errors generated by magnetorheological finishing (MRF) to validate the model. Simulation result of the smoothing rates of the errors after each smoothing process matched well with the experiment results.
The good agreement of the theoretical ratio with the experiment result proves that the proposed model is of for different multi-layer polishing tools during smoothing different mid-spatial frequency errors.
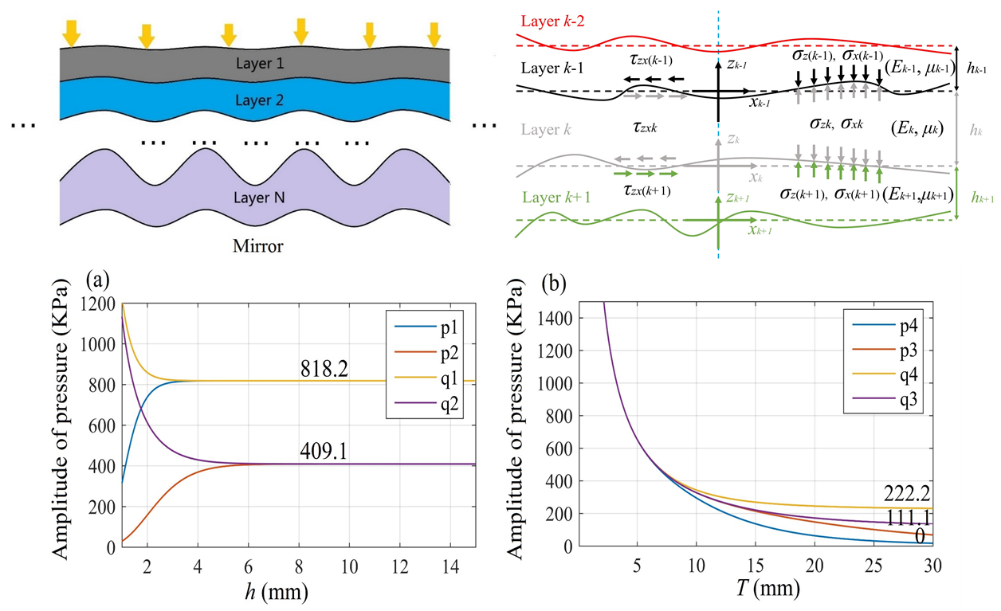
The model and result of pressure amplitude (Image by SIOM)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

