
Yb3+-doped silica fibers have been one of the most important gain mediums for high-power laser applications due to their high efficiency and good beam quality. However, the fabrication of the key material - Yb-doped silica glass with good radiation resistance performance and high doping concentration is a big challenge.
Recently, a research group from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences investigated the effect of AIPO4 join concentration on optical properties and radiation performance of Yb-doped silica glass. The results were published in Journal of Applied Physics.
Through a modified sol-gel method, the researchers prepared a series of Yb-doped silica glasses containing equimolar amounts of P2O5 and Al2O3. The ratio of Al and P was precisely controlled close to one.
The study showed that the sol-gel process was conductive to improve the dispersity of co-dopants in silica glass. With spectroscopy and electron paramagnetic resonance measurements, researchers found that the increase of AIPO4 join concentration in Yb-doped silica glass led to a decrease in the refractive index with a factor of 1.1*10-4, a decrease in Yb clusters concentration and meanwhile an improved radiation hardening performance.
These results demonstrated that fiber laser performance could be less vulnerable to Yb clusters and ionizing radiations and therefore provide basis for refractive index control in fiber core and contribute to the design of Yb-doped large mode area silica fiber.
It is hoped that Yb-doped silica glass with a high concentration of AIPO4 join may have potential applications in high-power space fiber lasers.
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China.
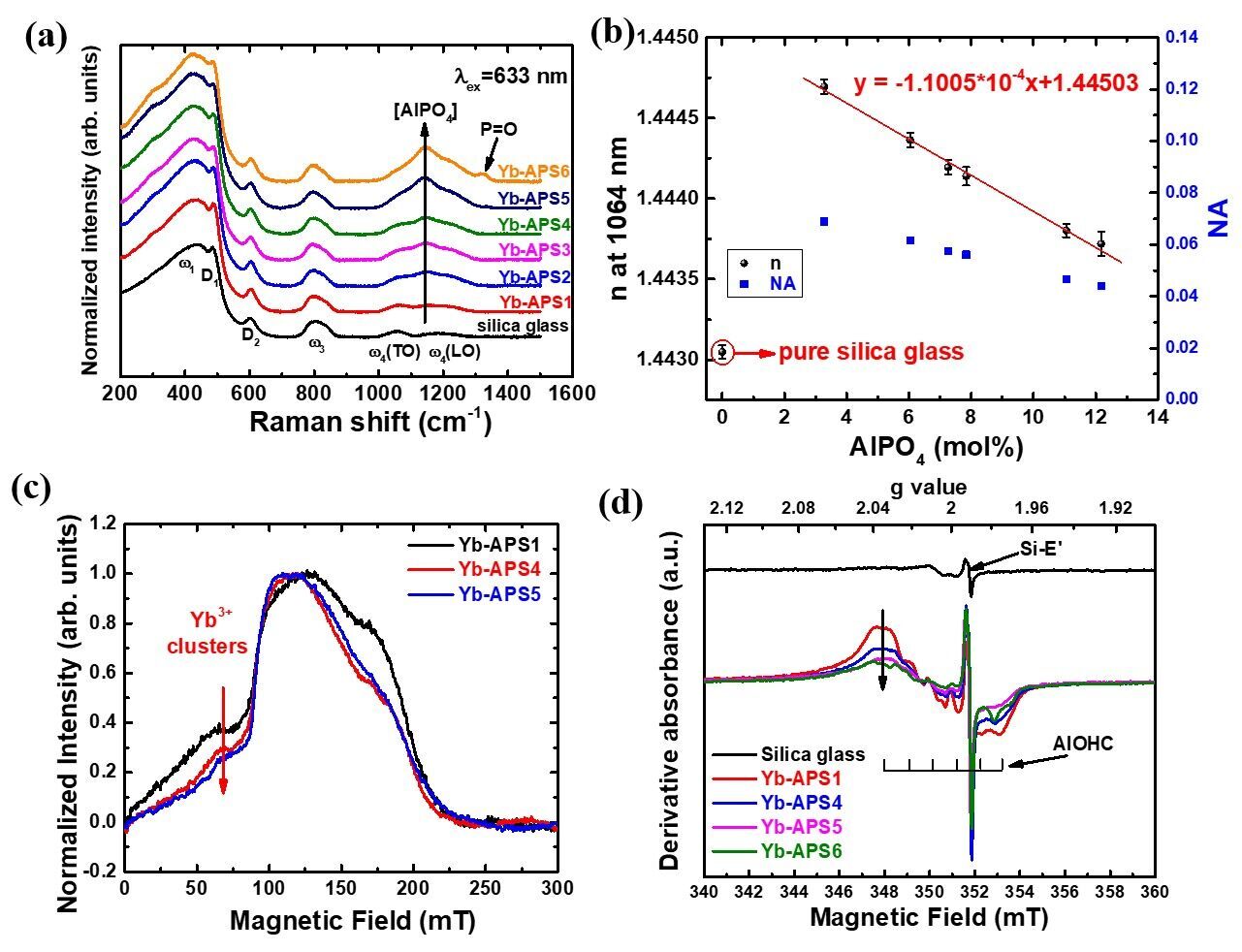
The influence of AlPO4 join (Image by SIOM)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

