
Chinese scientists conducted researches on 2.7-3 μm mid-infrared laser crystals and they achieved improvements of laser performances on mid-infrared crystal by co-doping ions.
This work was completed by SUN Dunlu’s research group with Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science.
2.7-3 μm mid-infrared lasers have been widely used in biomedicine, atmospheric detection as well as other scientific research fields.
Through their work this time, they grew Er:YAG and Cr,Er:YAG crystals by the Cz method.
In addition, they also characterized the crystalline qualities, spectra, laser performances, and beam qualities of the two crystals and made a comparison.
They obtained a maximum single pulse energy of 1.52 J on the Cr,Er:YAG crystal operated at 5 Hz and 2.94 μm, corresponding to the slope efficiency and electrical-to-optical efficiency of 1.80% and 1.28%, but those of the Er:YAG crystal were only 0.99 J, 1.31% and 0.83%, respectively.
Their study results show that the co-doping of Cr3+ can make the single pulse energy and efficiency of 2.94 μm mid-infrared laser on the Cr,Er:YAG crystal improved obviously.
These works are significant for improving the laser performances of 2.7-3 μm mid-infrared laser crystal and promoting practical applications.
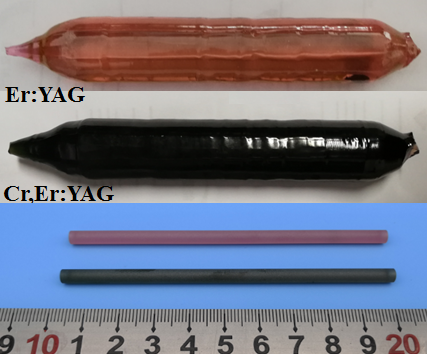
Fig.1 Photograph of the Er:YAG and Cr,Er:YAG crystals and the processed laser crystal rods (Image by ZHANG Huili)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

