
The Beijing-Arizona Sky Survey (BASS) is an ambitious wide-field multicolor survey of 5000 deg2 of the Northern Galactic Cap using the 2.3m Bok Telescope at Kitt Peak. This is a four-year international collaboration project between the Chinese team led by National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) and the U.S. team led by Steward Observatory, University of Arizona.
The survey observation started on January 7, 2015. It lasted about 4 years and ended on February 13, 2019. The BASS team finished 375 scheduled nights to complete three passes of the foot-print in two bands.
The completion of the survey enables to produce a new legacy imaging dataset, with scientific impact comparable to the original SDSS imaging survey. It is expected to become the leading imaging survey of the Northern Galactic Cap for the foreseeable future.
It can also provide unique science opportunities in a wide range of topics in galactic and extragalactic astronomy, including galactic structure, near-field cosmology, AGN evolution, high redshift quasars, large scale structure of the universe and time-domain astronomy.
Since its initiation in 2014, the BASS project has obtained supports from the Chinese Telescope Access Program, the International Cooperation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Prof. ZHOU Xu and Associate Professor ZOU Hu at NAOC and Prof. FAN Xiaohui at University of Arizona (UA) are involved in the survey. The BASS uses the Bok Telescope to survey the North Galactic Cap with g and r bands. The survey depths are g=24 and r=23.4 mag for 5σ extended sources. It is about 2 magnitudes deeper than the SDSS imaging survey. One of the key goals is to provide input catalogs for the up-coming project of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), which will be initiated in 2020.
The BASS is an open survey, which has no data protection. The raw data are immediately released after they are taken and can be accessed in NOAO Science Archive and China-VO. There have been three releases of the BASS data, including calibrated images and catalogs. The latest release is DR2. The final release will be ready this summer. The BASS data are also involved in the DESI imaging data releases, which are designed for DESI target selections.
Based on the imaging data, the BASS team and collaborators have performed substantial studies such as high-redshift quasars, strong gravitational lenses, galactic clusters, low surface brightness galaxies, galactic structure, variable stars and AGN. Some BASS members have become the DESI members and will carry out further international collaborations.
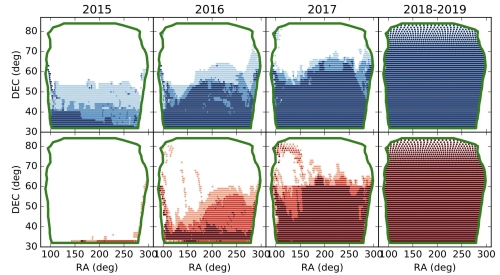
Figure. Yearly observing progress of the BASS. The red is for g band and the blue is for r band. For each point, there are three exposures. Darker color represents for more exposures. (Image by NAOC)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

