
Newsroom
A research team led by Prof. ZHANG Tianshu from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a low-stress electro-optic switch based on large-aperture β-barium borate (BBO) slab crystals and integrated it into an Nd:YAG hybrid-cavity Innoslab laser system.
The results, published in Optics Express on January 13, address long-standing challenges in high-energy laser systems, particularly those related to switching modulation consistency and operational stability.
High-energy, high-repetition-rate laser systems place demanding requirements on electro-optic switches, which must withstand significant thermal and mechanical stresses. These factors can adversely affect modulation performance and beam quality, presenting a key challenge to achieving stable, high-quality laser output.
In this study, the researchers introduced a low-stress packaging design and improving electric-field uniformity, achieving enhanced electro-optic modulation performance. As a result, the Nd:YAG Innoslab laser delivered stable, high-energy pulsed output under both continuous and pulsed pumping modes, while maintaining near-diffraction-limited beam quality.
Additionally, the researchers employed a stable–unstable hybrid cavity configuration and optimized the matching between the pump beam, slab laser crystal, and Q-switch to mitigate thermal effects that typically limit laser performance.
Combined with investigations into beam homogenization and high-speed electro-optic modulation, these advances enabled precise control of laser operation and further improved the compactness and overall performance of high-power laser systems.
This achievement lays a solid foundation for future applications, including high-repetition-rate laser sources and satellite-based lidar systems, and represents an important step forward in high-energy laser technology, according to the team.
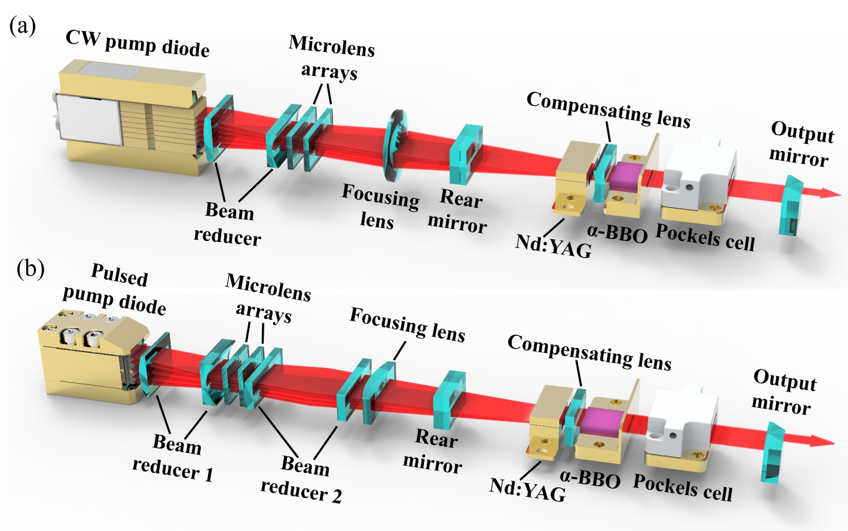
Schematic of hybrid Innoslab laser system. (a) continuous-wave pumping. (b) Pulsed pumping. (Image by CHEN Jinxin)
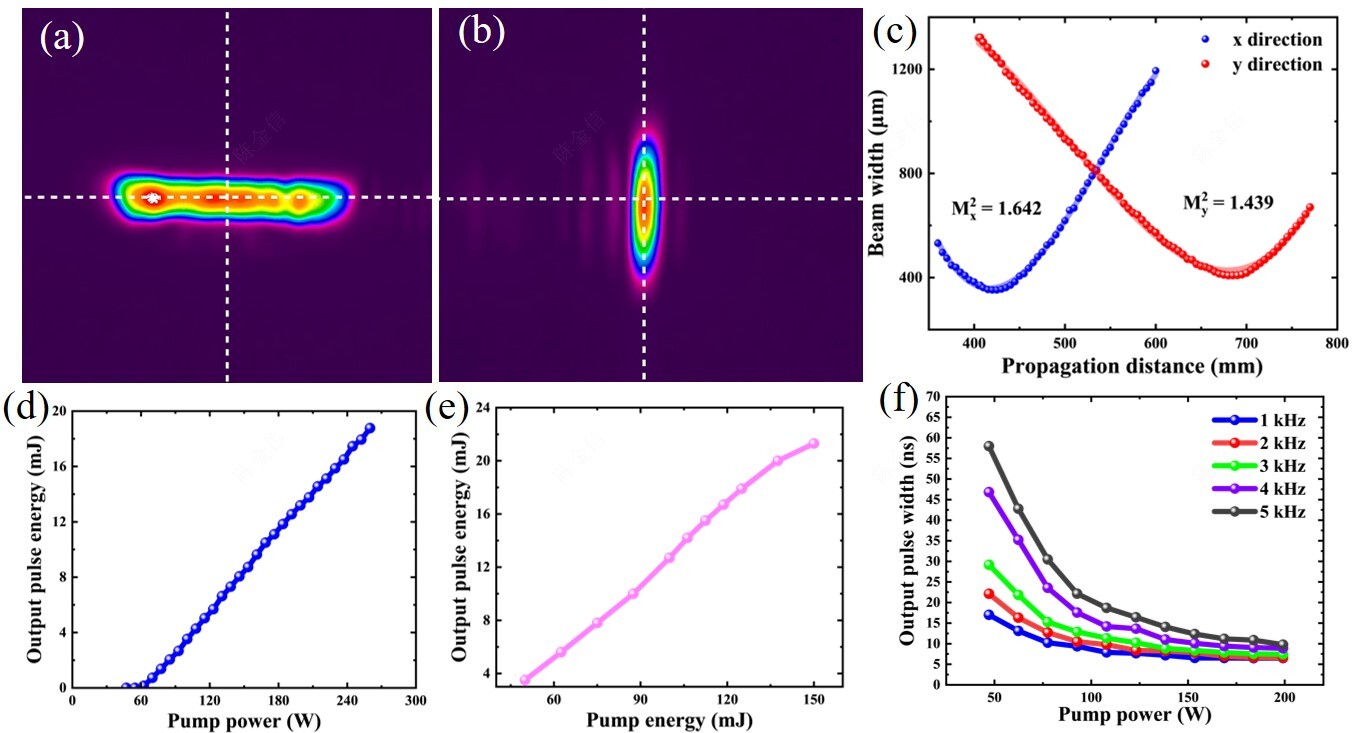
Laser output characteristics include beam profile, output pulse energy and beam quality. (Image by CHEN Jinxin)
