
2024
~ 2-μm near-infrared lasers are crucial in medical surgery, lidar, and other scientific research areas. These lasers can be created by exciting a crystal doped with Tm³⁺ ions using a 795 nm laser.
For Tm-doped crystals, high-power lasers can be produced by using end pumping. But when the power gets too high, heat builds up unevenly in the crystal, distorting the laser beam and reducing its quality. Currently, various methods have been proposed to mitigate or compensate for the thermal effects in crystals.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. SUN Dunlu at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciencesemployed single-end pumping method for four different types of Tm:YAP crystal rods and achieved superior laser performance using a concave YAP/Tm:YAP/YAP bonding rod.
Thermal bonding combined with concave end-face processing was applied to Tm:YAP crystal rods for the first time, resulting in the fabrication of four different types of crystal rods: flat Tm:YAP rod, flat YAP/Tm:YAP/YAP bonding rod, concave Tm:YAP rod, and concave YAP/Tm:YAP/YAP bonding rod.
When testing the laser performance of each rod with a single-end pumping method, the researchers found that using YAP matrix crystals as bonded end-caps helped improve heat dissipation, while the concave end-face design effectively reduced the thermal lensing effect.
The concave YAP/Tm:YAP/YAP bonding rod stood out by increasing the maximum laser output power from 36.56 W to 42.5 W and improving efficiency by about 4% compared to the flat Tm:YAP rod. Under high power and extended use, it also remained crack-free, unlike the flat Tm:YAP rod that showed signs of cracking.
Additionally, the concave YAP/Tm:YAP/YAP bonding rod produced the highest quality laser beam, as indicated by the smallest M2 factor among the four rods.
Their work suggested that combining thermal bonding with concave end-face processing effectively enhances the heat dissipation capacity of Tm:YAP lasers and reduces thermal lensing effects, thereby enabling high-performance near-infrared laser output.
Related findings were published in Optics Express.
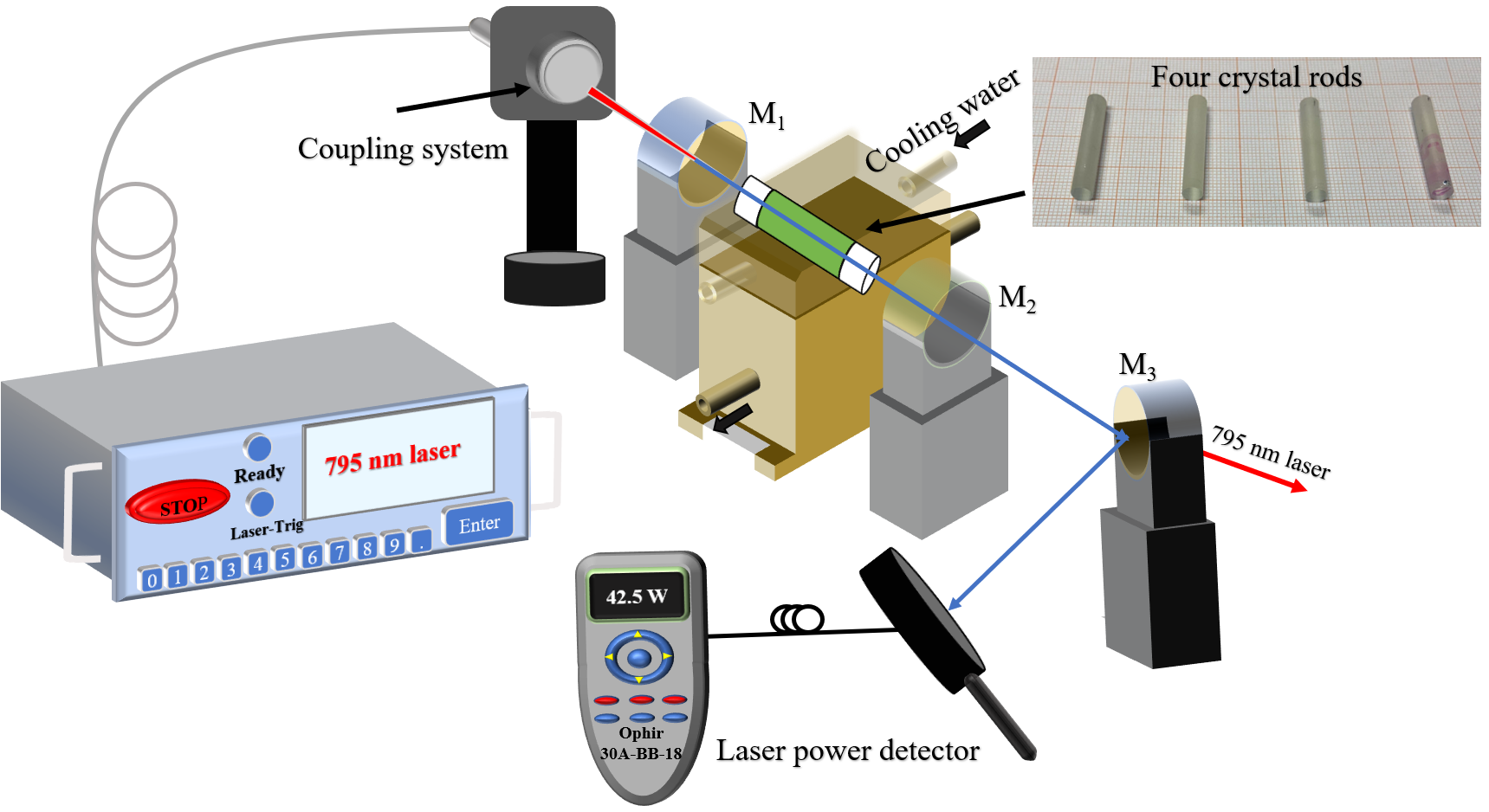
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the LD end-pumped four kinds of crystal rods (Image by DONG Kunpeng)
