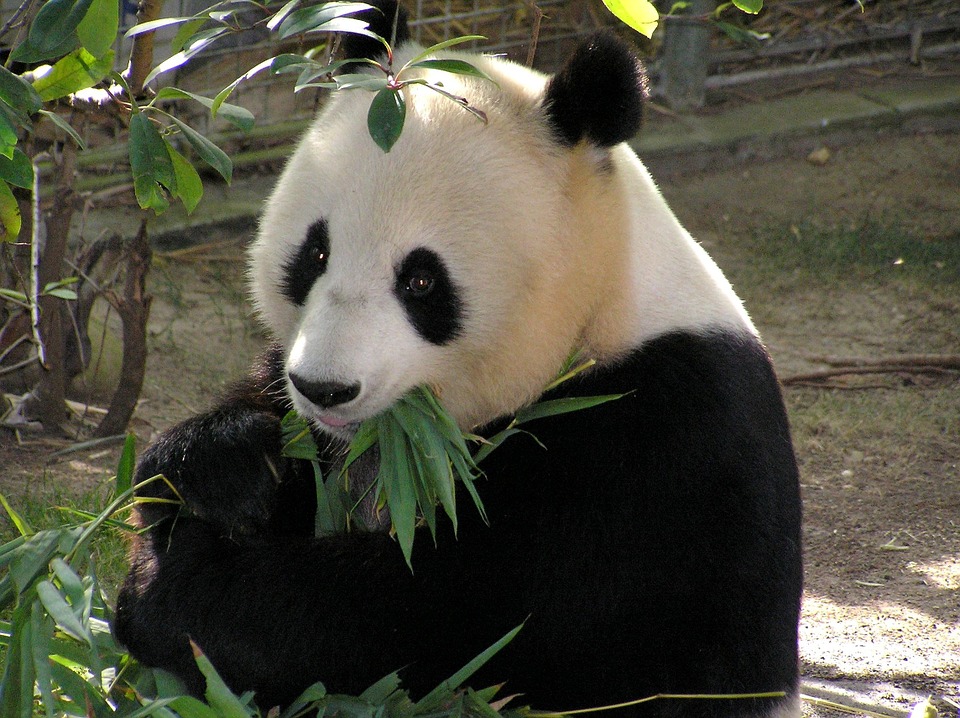


Despite feeding almost exclusively on bamboo, the nutrients that giant pandas consume and absorb most closely resembles that of carnivores, a joint Chinese-Australian study revealed on Friday. The study by the University of Sydney (UoS) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) showed that 50 percent of the pandas' energy intake comes from protein, a similar figure to wolves and feral cats.
Chinese researchers found that a compound, previously investigated for the treatment of head-and-neck cancer, might be a lead compound for the development of drugs to treat hepatitis A virus infection. The study reported four potent hepatitis A virus-specific neutralizing antibodies that efficiently inhibit hepatitis A virus infection by blocking the virus's ability to attach to the host cell.
Chinese scientists have found that a lack of circular RNAs may spin the immune system out of control and lead to lupus, suggesting new thoughts in lupus treatment. A research team of scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and doctors from Renji hospital of the school of medicine of Shanghai Jiaotong University found that people with lupus have lower-than-normal levels of circular RNAs, triggering an immune reaction meant to fight viruses.
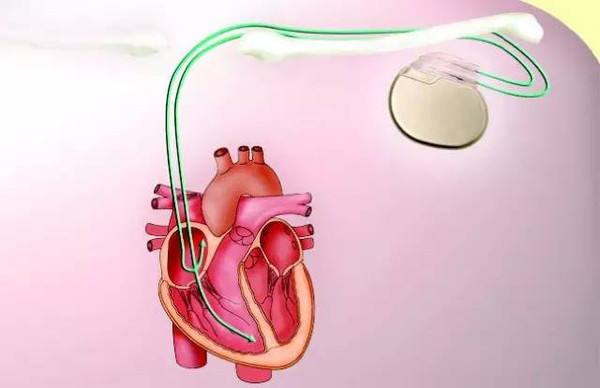
A research team has developed an implantable medical device that can harvest energy from heartbeats rather than batteries, according to a recent report published in the journal Nature Communications. The cardiac pacemaker was designed on the basis of an implantable triboelectric nanogenerator, which can achieve energy from heartbeats and convert the energy to electricity for powering pacing pulses.
Chinese researchers have developed a new catalyst to convert carbon dioxide, the main greenhouse gas, into methanol, widely considered a clean fuel for engines. A research team, led by Zeng Jie with the University of Science and Technology of China, developed a catalyst based on single atoms of platinum, which can effectively turn carbon dioxide into methanol under an atmospheric pressure of 32 bars and at 150 degrees Celsius.
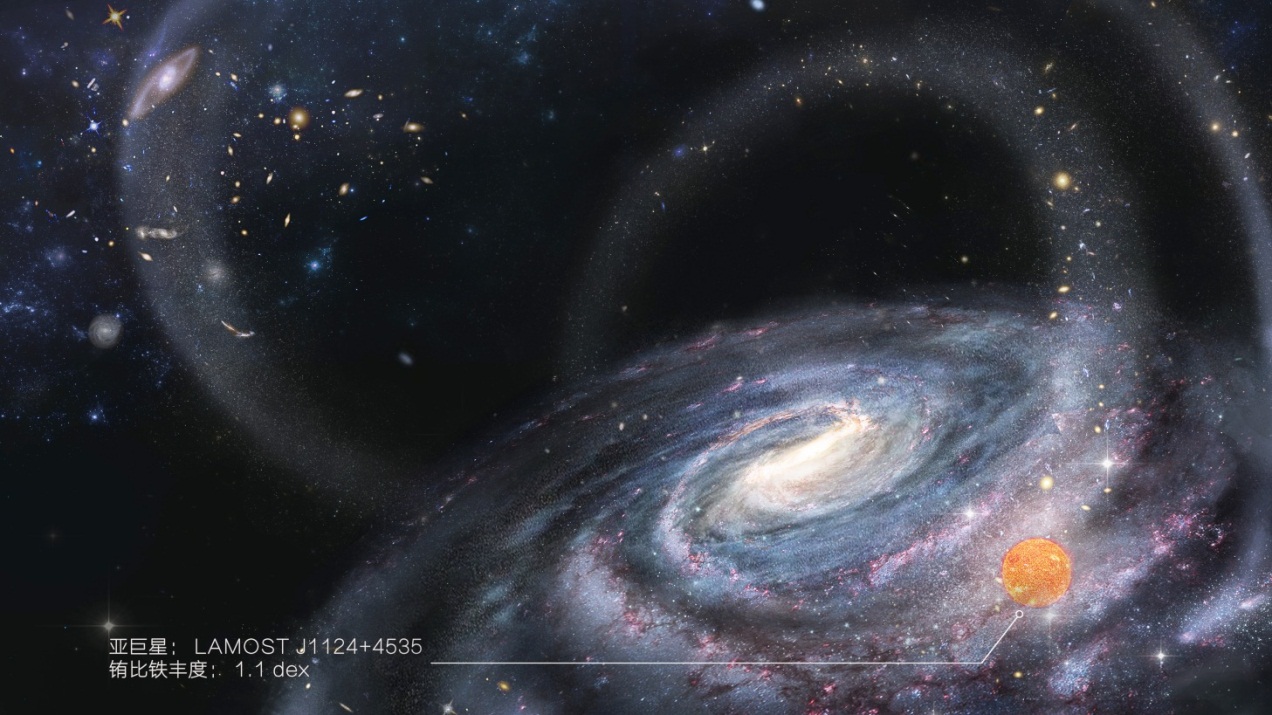

A team of Chinese and Japanese astronomers found that a special star within the Galactic halo was originated from a dwarf galaxy, which was disrupted and "swallowed up" by the Milky Way. Small stellar systems like dwarf galaxies are believed to be the main building blocks of our galaxy. However, it is unclear how many and what kind of stars in our galaxy are originated from satellite dwarf galaxies.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

