
Newsroom
Scientists have for the first time seen clearly the dynamic structure of the receptor of human parathyroid hormone, of which the secretion is closely related to diseases including osteoporosis, hypoparathyroidism, and cachexia.
The revelation provides valuable insights into discovering novel therapeutics against such diseases, the group of researchers said at a media briefing on Friday.
Patients of osteoporosis, who the National Health Commission in October said number nearly 20 percent of Chinese over the age of 50, need to take medicines stimulating the human parathyroid hormone receptor.
As such medicines are polypeptide, they can only be injected rather than being orally taken, which can trigger a reaction with enzymes in the mouth and become ineffective, researchers said.
"The successful viewing of the dynamic structure enable us to see clearly which exact position the hormone goes into the receptor as well as the corresponding reactions happening to the downstream signaling proteins and the surroundings," said Zhao Lihua, one of the leading researchers on the team and an associate professor from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
"It will allow scientists to screen small-molecule compounds that fit this exact position. If this succeeds, researchers can continue to develop oral drugs," she said.
A paper about the study conducted by CAS' Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica in collaboration with researchers from Zhejiang University School of Basic Medical Sciences and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine was published on the website of United States-based journal Science on Friday. (China Daily)
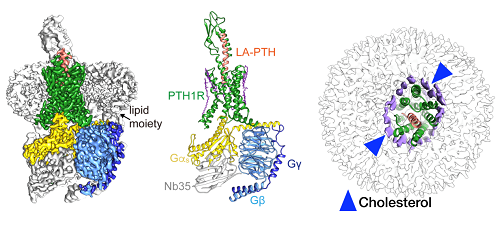
Cryo-EM structure of the human parathyroid hormone receptor-1 signaling complex. (Image by Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica)
