
2024
The inherent flexibility and conformational dynamics of RNA molecules pose significant challenges for traditional structural techniques, such as X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and cryo-electron microscopy, in resolving RNA structures and capturing RNA's dynamic changes.
Combining multiple methods and integrating experimental data with computational modeling can expand the research approaches and perspectives within structural biology.
Prof. FANG Xianyang from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, reviewed three complementary molecular ruler techniques in Current Opinion in Structural Biology on October 22, including electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), X-ray scattering interference (XSI), and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET).
Prof. FANG elaborated on the fundamental principles of these three techniques and demonstrated how to use the NaM-TPT3 unnatural base pair system to achieve site-specific labeling of long-chain RNA, allowing for nanoscale measurements of intra- and intermolecular distance distributions in RNAs.
This labeling method overcomes the limitations of traditional RNA labeling techniques concerning RNA length and labeling sites. "It offers advantages such as high reaction efficiency, simplified purification, and the elimination of denaturing conditions during purification, thereby enabling the study of long-chain RNA structures and conformational dynamics using molecular ruler techniques," said FANG.
By showcasing the application of various molecular ruler techniques in studying the structure and conformational dynamics of flaviviral RNAs, this research not only provided a more accurate understanding of the conformational changes in flaviviral RNAs but also identified new targets and strategies for treating viral diseases.
Additionally, the application of these techniques holds promise for advancing RNA nanotechnology, offering more possibilities for future biomedical research, according to FANG.
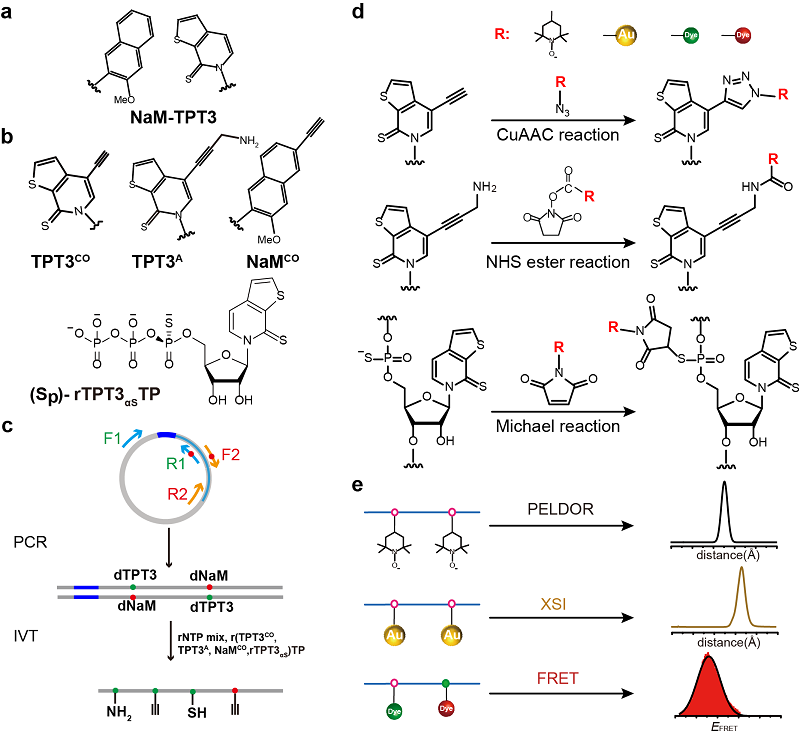
The NaM-TPT3 UBP-based site-specific labeling method for long-chain RNAs (Image by FANG Xianyang's group)
