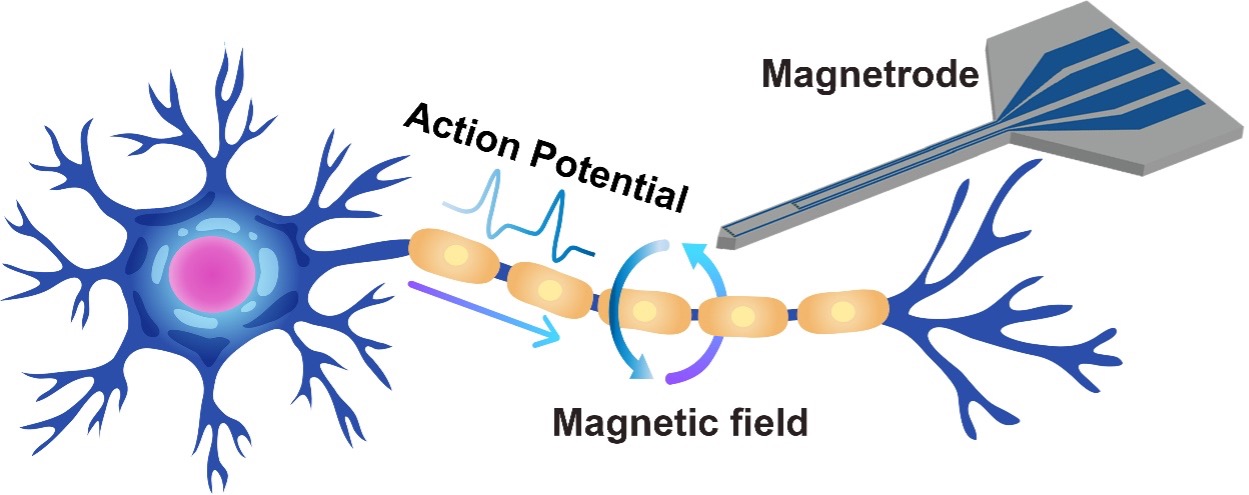
The quest to understand the intricacies of the human brain has led scientists to explore innovative techniques for monitoring neural activity. Additionally, the detection of weak magnetic signals generated by neurons during neural communication has garnered significant attention.
Magnetoresistance (MR) sensors, known for their compact size and exceptional sensitivity, have emerged as promising candidates for detecting those weak magnetic signals. Specifically, tunnel magnetoresistance (TMR) sensors, with their ultra-high sensitivity, have the potential for the scientists to revolutionize their ability to study brain function.
Researchers from the Aerospace Information Research Institute (AIR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences introduced a novel TMR-based magnetrode design that aims to revolutionize local magnetic field detection in the brain. The findings were published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
These magnetrodes, which integrate TMR sensors with needle-shaped silicon substrates, are designed to be inserted into the brain for in-situ monitoring.
To optimize the performance of the magnetrodes, the researchers explored various design parameters such as aspect ratios of the free layer, junction shapes, quantities, and serial arrangements. Through a custom-built magneto-transport and noise measurement system, they characterized the magnetrodes and achieved a remarkable limit of detection of 300 pT/Hz at 1 kHz. This remarkable sensitivity suggests that neuronal spikes, which are typically difficult to detect with traditional methods, can now be distinguished with minimal averaging.
This study not only demonstrates the great potential of magnetrodes to detect weak magnetic signals in biological systems, but also provides a new tool for understanding brain function and neural communication mechanisms.
With further technological development, TMR-based magnetrodes are expected to play a greater role in neuroscience, biomedical engineering, brain computer interface, artificial intelligence and other related fields.
Schematic diagram of magnetrode to detect magnetic fields generated by action potentials. (Image by AIR)