
2024
The deterioration of global ecosystems and environmental problems, such as global climate warming, extreme weather events, and severe pollution threaten the human environment. Implementing pro-environmental behaviors is one of the effective ways to solve environmental problems. How to promote behavioral change and implement more pro-environmental behaviors through family education has become a social research focus.
In order to explore family-based strategies to effectively promote pro-environmental behavior, a research team led by Dr. LIU Pingping from the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted an empirical study on children (11-14 years old) and their families (416 pairs of valid data on parents and children). They revealed a positive impact of parent-child interaction on pro-environmental behavior, and also the potential impact mechanism of family well-being and natural connectedness based on the actor-partner interdependence mediation model.
This study was published in Current Psychology on Jan. 9.
The researchers found that parent-child interaction has a positive impact on intergenerational relationships and family well-being. The higher the level of interaction, the greater the sense of family well-being felt by both parents and children, and the higher the level of connectedness to nature. Happy people are more likely to engage in pro-environmental behavior. Therefore, people's pro-environmental behavior could be influenced by family well-being.
That is, parent-child interaction increases the family well-being and nature connectedness of parents and children, thereby promoting the improvement of their pro-environmental behavior.
In addition, the family is the basic unit of social composition, and parent-child interaction can promote the pro-environmental behavior within family. It is possible to spread pro-environmental behavior among families through the participation of schools, communities, and other departments, and ultimately achieve "universal environmental protection".
"Individuals, families, schools, and communities should organize parent-child activities with environmental protection as the theme, strengthen parent-child interaction, and promote family well-being and pro-environmental behavior," said Dr. LIU Pingping, corresponding author of the study.
This study reveals the direct effect of parent-child environmental interaction on pro-environmental behavior, as well as the indirect relationship between parent-child interaction and pro-environmental behavior through family well-being and nature connectedness.
These results suggest that parent-child interaction is an effective way to promote family well-being and nature connectedness, thereby increasing parents' and children's pro-environmental behavior. The research results not only provide theoretical support at the family level for the construction of ecological civilization, but also provide feasible practical suggestions for the creation of green families.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and the Scientific Foundation of the Institute of Psychology, etc.
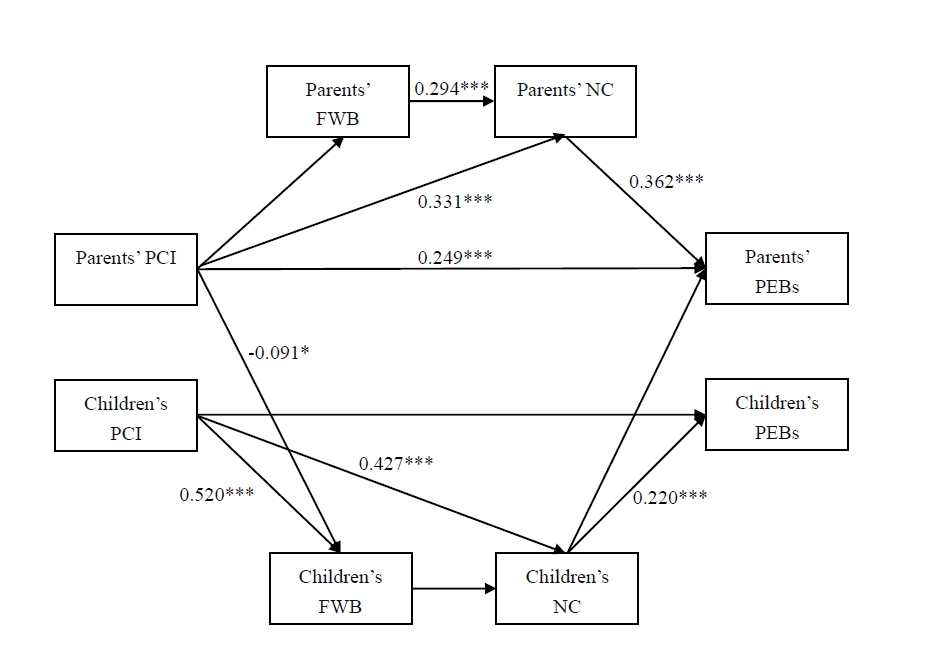
Actor-partner interdependence mediation model results for the direct association between PCI and PEBs. (Image by DING Mengyan)
