
A liquid metal killing robot-T1000 shows a very impressive self-healing function in the film Terminator 2 in 1991. Can you imagine that one day we can produce such self-healing materials for heavy-duty protection and wearable electronics? Recently, scientists make a step forward towards this dream-new synthetic strategy for supertough healable polymers.
Materials can be endowed with dynamic reversible properties by introducing the weak supramolecular interactions. However, to realize self-healing function, materials must be soft enough for reconstruction, which limits their further applications. Thus, it's still a great challenge to find efficient approach for self-healing materials with strong mechanical properties.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Guoliang at the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences found a new strategy for supertough self-healing materials. Its findings entitled "Towards Dynamic but Supertough Healable Polymers through Biomimetic Hierarchical Hydrogen Bonding Interactions" was published in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.
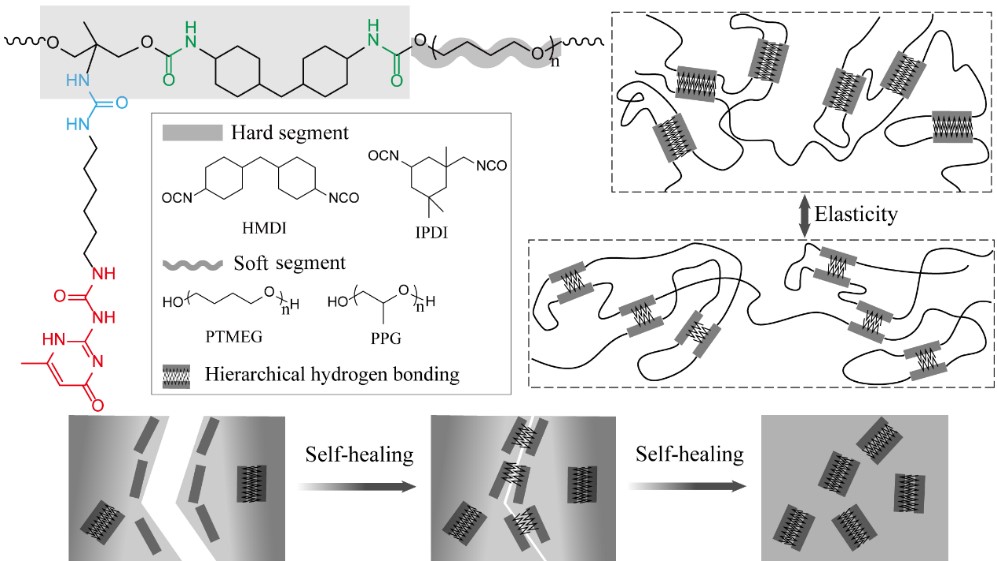
Figure 1. Illustration of the self-healing polyureathane via biomimetic synthetic strategy with hierarchical hydrogen-bonding interactions (Image by SONG Yan)
It is well-known that titin molecules in biological system is capable of self-healing when muscle is damaged. Furthermore, the protein molecules have exceptional toughness. The unique molecular structure and supramolecular hydrogen bond interactions contribute to its excellent performance.
Similar to the molecular structure of titin, the researchers developed self-healing materials with supertough function, as a diol molecule with hierarchical hydrogen bonds (Figure 2) was introduced into the polymeric molecular structure. The as-synthesized polymers exhibited not only self-healing properties, but also high tensile strength and super toughness with large deformation and resilience.
When the damaged film was healed, the transparent film could still easily lift up to 10kg of weight, and be quickly recovered (video 1). For the self-healing materials with hierarchical hydrogen bonding interactions, the tensile strength and toughness was up to 44 MPa and 345 MJm-3, respectively.
This is the maximum value of healable materials reported so far in literature. The mechanism of hierarchical hydrogen bond interactions was characterized by in-situ variable temperature infrared spectrum, and the micro-phase separation structure was verified by small angle scattering method. This research provides a unique perspective for the molecular design of intelligent self-healing materials.
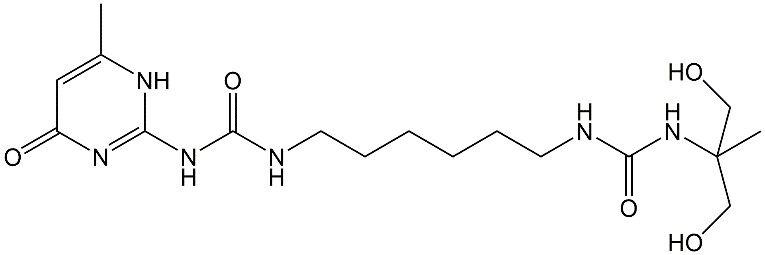
Figure 2. The synthesized diol molecule with UPy and urea two segment (U2-diol) (Image by SONG Yan)
Video 1. Supertoughness of healable materials (Video by SONG Yan)
Considering the wide use of healable materials, the researchers are trying to commercialize the developed diol molecule and the healable polymer materials. This biomimetic synthetic strategy for supertough healable polymers via hierarchical hydrogen bonding interactions brings new insights to self-healing materials.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

