
High-resolution images of sun's granulation structure and sunspot at near infrared (NIR) wavelength were captured through 37-element solar adaptive optics (AO) NIR prototype mounted the 1-meter infrared solar tower of Yunnan Observatory Feb. 24th and Mar. 3rd, 2011, shown in Fig. 1 and Fig.2. The research work was made by the solar AO team of CAS Key Lab. of AO from Institute of Optics and Electronics (IOE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). The breakthrough will improve our solar physics research. The images and observations will allow solar physical scientists to improve the accuracy of space weather forecast.
The research team overcame the challenge that conducts accurately wavefront detection and adaptive correction using solar granulation structure of such low contrast extended target for large aperture telescope. After adaptive optics correcting,the contrast of the solar granulation structure and sunspot images is significantly improved and the umbra and penumbra of sunspots is visible. The successful development of the demonstration system will lay a foundation for practical AO system from visible to NIR to 1-meter IR solar tower. We firmly believe that the "adaptive optics" glasses for the 1-meter infrared solar tower will produce a lot of high resolution data and enable the research on solar physics to international advanced level.
The sun is the source of light and heat on earth. Thus, the activity of sun contributes the earth weather and space environment as well other. In addition, the sun is the nearest star to the earth. Human being can learn more about other stars, galaxies and the universe through the research on sun. Solar magnetic field is the driver of solar activity. Research on the solar magnetic field is needed to obtain high-resolution image data. Large-diameter solar telescope equipped with AO systems promise solving this challenge.
During 1998 to 2001, under “the application of adaptive optics in high-resolution solar observation” --a key program of National Natural Science Foundation of China,CAE Member JIANG Wenhan and Research Prof. RAO Changhui et al built the first tip-tilt correction AO system for solar observation. The system was mounted on the 43-cm solar telescope of Nanjing University. The experimental study was conducted on low-order correction AO compensation performance. It was showed that the precision of tracking sun image had been improved and image jitter diminished.
With the coming of the 24th peak-year of solar activity, solar activity is increasing, which provides the best opportunity to us. The 1-meter infrared solar tower is the main instrument for observation of solar physics and space weather forecast in the early 21st century. The aperture and performance reached to leading level in the world. The solar tower is located near Fuxian Lake in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province that is one of the world's best sites for solar observation. It is necessary to mount AO systems to not only meet the requirements of the international development of solar physics but also further improve the level of solar physics research. The AO demonstration system used to observations is the upgrade the AO system on the fine structure 26 cm solar telescope of Yunnan Observatory in 2009.
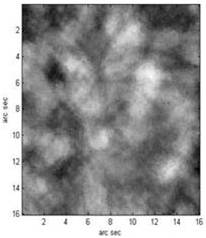
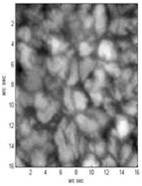
(a) AO off (b) AO on
Fig.1:The observations of solar granulation Structure, at 1555nm wavelength (Image by CAS Key Lab. of AO IOE, CAS)
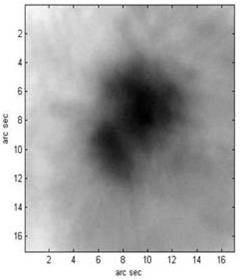

(a)AO off (b) AO on
Fig.2:The observations of sunspot, at 1555nm wavelength (Image by CAS Key Lab. of AO IOE, CAS)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

