
Anyons form the basis for topological quantum computation and error correction, where the topological aspect of anyonic braiding is one of the important features that gives rise to fault tolerance. More qubits to control will assist researchers to explore further.
In a recent study published in Optica, a research group led by Prof. PAN Jianwei and LU Chaoyang from University of Science and Technology of China of Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully designed the largest planar code platform at present using photons, and demonstrated path-independent property in optical system for the first time.
Researchers first generated the eight entanglement photons using spontaneous parametric down-conversion and interference. One of the photons is encoded with polarization and path, eventually creating the nine qubits anyons models.
They then performed braiding operations on the anyons. Thanks to more qubits, the platform contains enough lattices for demonstration of path-independent property. If two operations have topologically equivalent paths, phase offset of system will remain unchanged. By measuring this offset, path-independent property was observed in the system.
Therefore, this study provided a platform for simulating the braiding operations with linear optics, and researchers are able to conduct more complicated experiments on the features of anyonic statistics in the future.
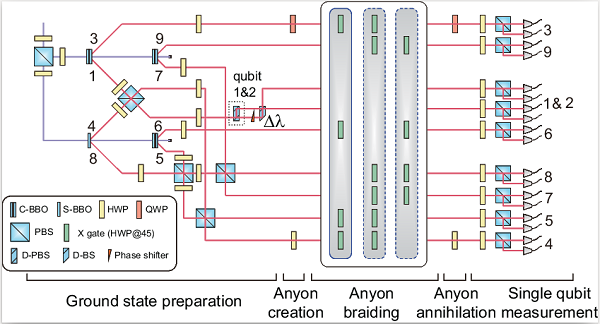
Setup of nine-qubit linear optical platform. (Image by LIU Chang)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

