
Recently, researchers from the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) applied a universal method via the red clump stars and measured the distances of 47supernova remnants (SNRs).
SNRs play a key role in the final evolution of stars, reshaping and heating interstellar medium, and the birth of the high-energy cosmic rays. Reliable distances to SNRs are essential to constrain their physical parameters like age, physical size, the expansion velocity and the explosion energy of the progenitor supernovae, which reveal the evolutionary process of SNRs.
However, it is challenging to obtain reliable distances of SNRs. Distance measurements of SNRs usually depend on specific conditions, for example, the SNRs might interact with the molecular clouds or be associated with the OB stars or pulsars.
The red clump (RC) stars are low mass stars in the early stage of core He-burning. They are used as standard candles and extinction probes to build the optical extinction - distance relation in each direction of SNRs with known extinction.
Combining the Bayesian method, the distances of 15 SNRs were well determined. Among them, the distances of G65.8-0.5, G66.0-0.0 and G67.6+0.9 were given for the first time. The researchers also obtained 32 upper/lower limits of distances, and the distances to G5.7-0.1, G15.1-1.6, G28.8+1.5 and G78.2+2.1 were constrained.
The study, published in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, was supported by the National Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
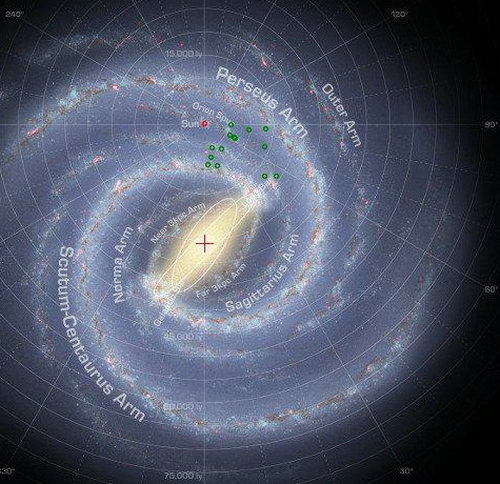
Supernova remnants are distributed in two dimensions on the spiral arms of the galaxy. The red dots indicate the sun, and the green dots represent supernova remnants. Background maps are galactic art maps based on existing observations. (Image by NASA/JPL-Caltech/R.Hurt)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

