
Laser, considered as the edge tool, has been commonly used in many fields.
To obtain better 2.7-3 μm mid-infrared radiation resistant laser, which is a kind of laser and is used in dental treatment, a chinese study team made a new design on the laser crystals. And the study result showed a higher efficiency of the crystals.
The recent study was conducted by SUN Dunlu's research group at Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science. Actually, it was further explored based on their previous work.
In the study, the team has uncovered the mechanisms in 2.7-3 μm mid-infrared radiation resistant laser crystals growth. And they further optimized the doping concentration of a new type of high efficiency and anti-radiation mid-infrared laser crystal Er,Pr:GYSGG.
According to the theoretical analysis by the team, the pure GYSGG crystal was bonded to the end-face of the crystal as a heat sink by using thermal bonding technology.
The study suggests that the design can accelerate the heat dissipation rate at both ends of the laser crystal rod, thus reduce the thermal lens effect effectively and greatly improve the laser performances of Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG crystals.
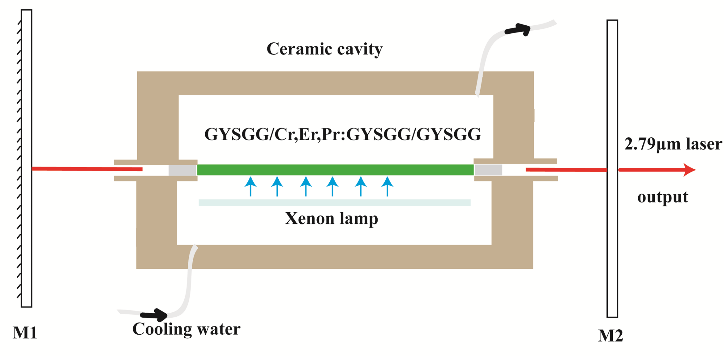
Schematic of the GYSGG/Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG composite crystal laser pumped by the xenon lamp. (Image by FANG Zhongqing)
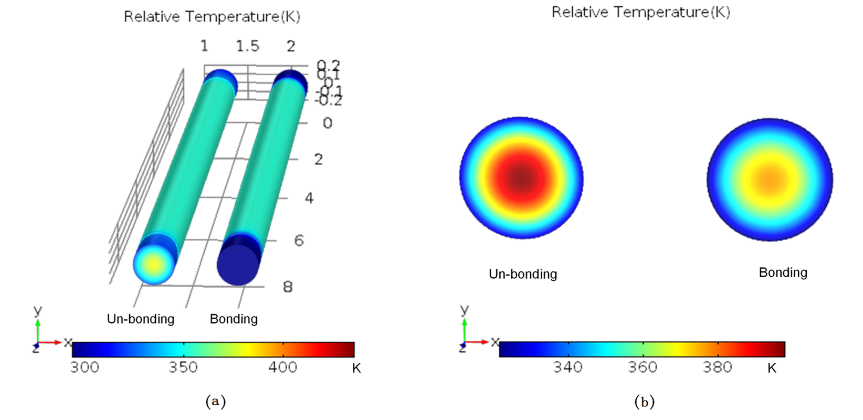
Relative temperature distribution models of single Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG crystal rod and GYSGG/Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG composite crystal rod. (Image by FANG Zhongqing)
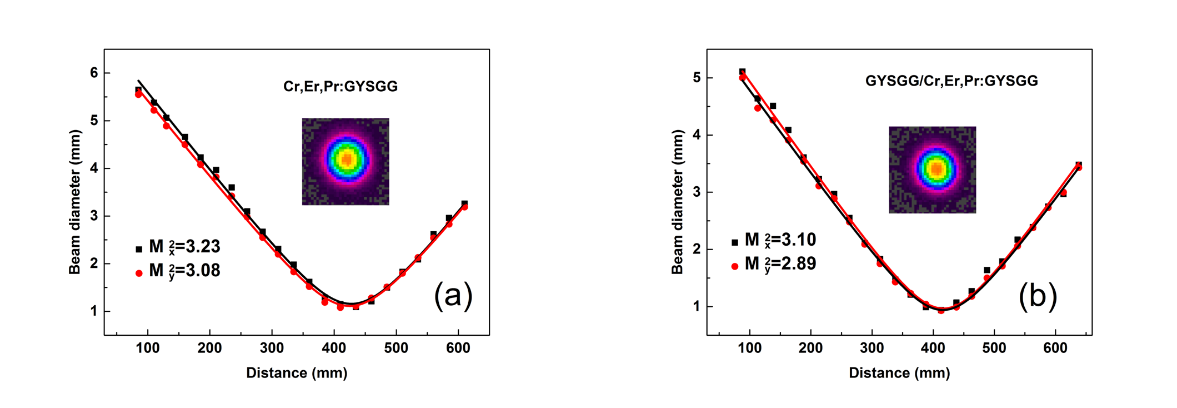
Beam diameter versus propagation distance of two crystals. (a) Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG crystal; (b) GYSGG/Cr,Er,Pr:GYSGG composite crystal. (Image by FANG Zhongqing)
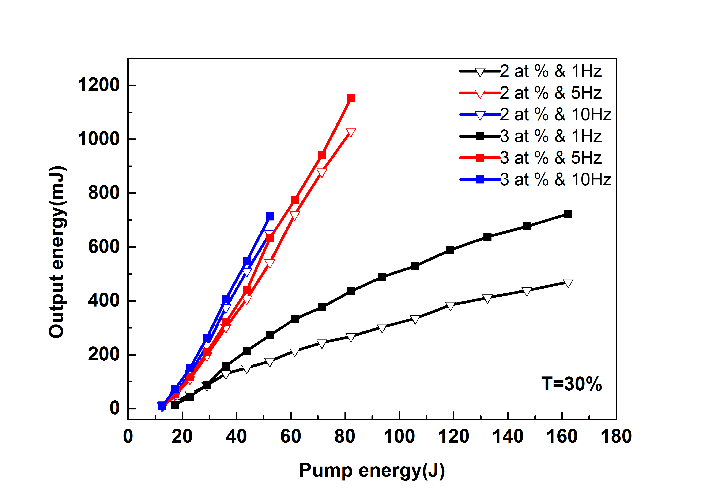
Output pulse energy versus pumping energy with different Cr3+ doping concentrations at T=30%. (Image by FANG Zhongqing)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

