
Prof. WANG Liping and Prof. TU Jie from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with researchers from City University of Hong Kong, recently discovered a new role of astrocytes in one of the basic cognitive functions - decision making.
Their findings, published in Cell Reports, could lead to new insights into functions of neuroglia cells in the cognition behavior.
The research team led by Prof. LI Ying from City University of Hong Kong provided an elegant cognition measurement model - gambling test.
Based on this model, they demonstrated that impairment of decision making is associated with suppressed synchronization in basolateral amygdala (BLA) - the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) network in the chronic pain rat models.
Prof. WANG Liping's team from SIAT is a pioneer group of optogentics in China. Through joint tackling, they found that the repairing effect of "astrocyte-neuronal L-lactate shuttle" on the impaired cognitive function: optogenetic activation of ACC astrocytes triggers local lactate release, which contributes to the rescue of BLA-ACC synchrony and decision-making performance in chronic pain rats.
Their findings proposed a new model for linking the basic neural cells metabolism function and advanced cognitive function.
Also, their findings provide new insights into cognitive and pain treatment in clinical chronic pain management.
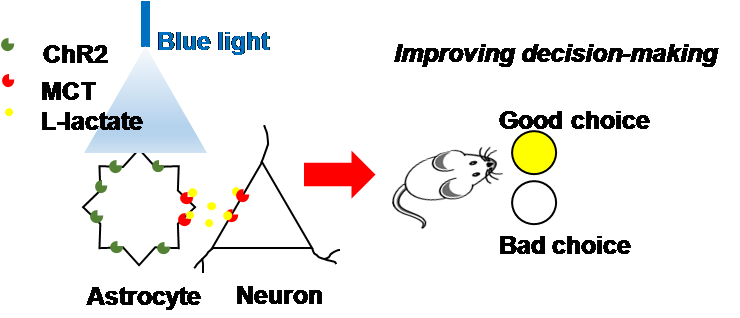
Impairment of decision making is associated with suppressed synchronization in basolateral amygdala (BLA) in the chronic pain rat models. (Image by SIAT)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

