
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a common whitening agent and is widely used in cosmetics, foods, and medicine. In the food industry, TiO2 is used as food additives, food packaging materials and auxiliary materials of diet.
Studies have found that about 10-36% of TiO2 particles in sweets like candy, chewing gum and cake were in the nanometer scale. Due to the unique nanometer-effects (such as size effect and surface effect), the bio-activity of nanomaterial is quite different from the same micron-material, which raises concerns about its potential health risk.
Recently, a research team led by Dr. WANG Hui from Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences identified that TiO2 nanoparticles in food could change the function of macrophages in a Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent manner which led to the disturbance of host immune balance. The study was published in Nanotoxicology.
Researchers observed the health effects of long-term intake of TiO2 nanoparticles which simulated the real exposure. They found that the long-term exposure to TiO2 nanoparticles from diets could decrease the chemotactic and phagocytic activity of primary macrophages and also induce macrophages towards pro-inflammatory activation which confirmed by the in vitro experiments.
In the sepsis model induced by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), mice feeding with TiO2 nanoparticles showed more severe symptom. However, in the TLR4 knockout and TLR4 independent models, TiO2 nanoparticles did not induce a significant adverse effect.
These results showed that TiO2 nanoparticles induced the abnormal activation of macrophages in a TLR4-dependent manner and could cause more adverse health effects under the external stimulation like infection.
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China.
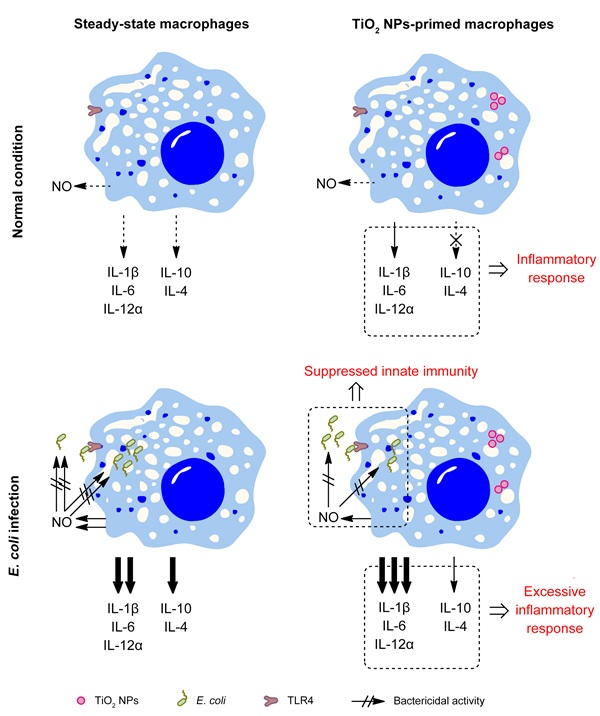
Figure: A schematic representation of the activating effects of TiO2 NPs on macrophages. (Image by Dr. WANG Hui’s lab)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

