
Chinese scientist Dr. DAI Haiming, of Center of Medical Physics and Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and his collaborators Dr. Scott Kaufmann and Dr. Meng X. Wei of Mayo Clinic were invited by F1000 Research to publish a review titled Mitochondrial apoptosis and BH3 mimetics, which summarized recent advances in understanding of the biology of BCL2 family members that shed light on the action of BH3 mimetics, reviewed preclinical and clinical studies leading to the regulatory approval of venetoclax, and discussed future investigation of this new class of antineoplastic agent.
This April, the BCL-2-selective BH3 mimetic venetoclax was approved to treat relapsed, chromosome 17p-deleted chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It culminates 30 years of investigation in many labs worldwide and this is a great victory for the whole field of cell apoptosis.
As a key regulator of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway, BCL-2 family attracts intensive attention. Through 3 decades of hardworking, several milestones have been marked, which includes the cloning of BCL2 at the t(14;18) translocation in follicular lymphomas, BCL2 inhibition of cell death, elevation of BCL2 in CLL and identification of venetoclax as a BCL2-selective BH3 mimetic.
Although the approval of venetoclax for CLL is a triumph in its own right, the challenge remains to optimize the use of this agent and other BH3 mimetics for improved therapy of diverse malignancies.
In this review, the authors summarize not only the mechanism of mitochondrial apoptosis, but also that of BH3 mimetic-induced killing. According to the review, binding of BH3 mimetics to anti-apoptotic BCL2 family members must result in BAX and/or BAK activation to elicit cell death.
And this BAX/BAK activation can occur by one of two processes (Figure 1): displace activator BH3-only proteins from anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members to drive Bax and Bak activation or directly substitute constitutively activated Bax and Bak from anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members.
In addition, the authors also made a summary and discussion on the main methods to predict BH3 mimetics sensitivity. In the end of this article, some future directions of this area are blueprinted, including screening of highly efficient inhibitors of Mcl-1 and digging new small molecular compounds that could directly activate Bax and/or Bak.
Faculty of 1000 was founded by publishing entrepreneur Vitek Tracz in 2000, aiming to tackle “deadly sins” in science publishing. F1000 publishes recommendations of articles in biology and medicine from a “faculty” of around 6000 scientists and clinical researchers and 5000 more junior associate faculty.
F1000 uses the individual scores to calculate the total scores for each article, which are used to rank the articles in each discipline. F1000 Research is an open access, open peer-review scientific publishing platform covering the life sciences.
Articles published not only have a peer-review process first, but also accept after-publication discussion. Different from most of the journals, the peer reviewer's names and comments are visible on the site.
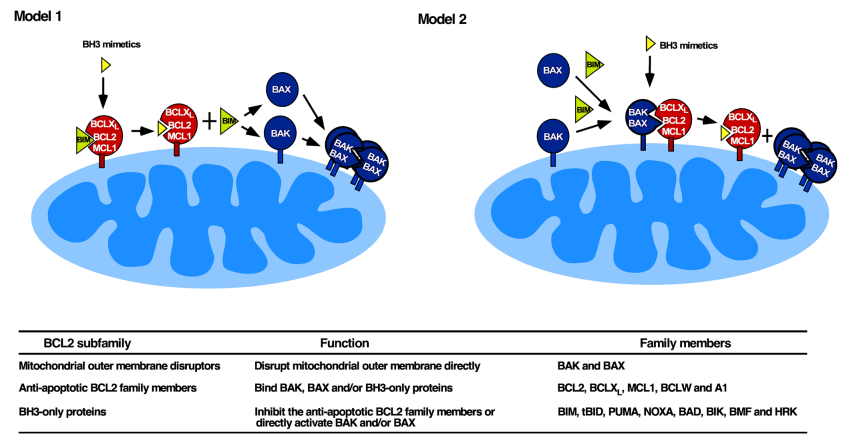
Two models of BH3 mimetic action (Image by DAI Haiming)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

