
Insulin resistance is a common feature of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Nutrients are important contributing factors to the development of insulin resistance in T2D patients. Previous studies have demonstrated that essential amino acids, particularly branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), are closely related to the development and prediction of insulin resistance in both human and animal models. However, whether non-essential amino acids and the enzymes involved in non-essential amino acids synthesis play roles in regulating insulin sensitivity remains unclear.
Phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1), an enzyme undertaking the second step of serine biosynthesis, plays an important role in colorectal cancer. A team of researchers led by Professor GUO Feifan at the Institute for Nutritional Sciences (INS), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences of Chinese Academy of Sciences, found that hepatic PSAT1 regulates insulin sensitivity via tribbles homolog 3 (TRB3), and serine might be involved in the regulation of insulin sensitivity.
To probe the role of PSAT1 in the regulation of insulin sensitivity, Dr. GUO and her colleagues examined the expression of PSAT1 in the insulin resistance animal models including db/db mice and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced insulin resistance mice. They found that hepatic PSAT1 expression is significantly reduced, and over-expression of PSAT1 by adenovirus expressing PSAT1 (Ad-PSAT1) ameliorates insulin resistance under both conditions.
The research demonstrated that PSAT1 regulates insulin sensitivity via TRB3 in vitro and in vivo, and serine is involved in the regulation of TRB3 by PSAT1. Liver serine level is significantly decreased in db/db mice and HFD mice, which suggests a possible role of serine in the regulation of insulin sensitivity.
This study provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance, and suggests that PSAT1 could be a possible novel drug target for treating insulin resistance.
This work entitled “Hepatic phosphoserine aminotransferase 1 (PSAT1) regulates insulin sensitivity in mice via tribbles homolog 3 (TRB3)” has been published on Diabetes.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Basic Research Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission and International S&T Cooperation Program of China.
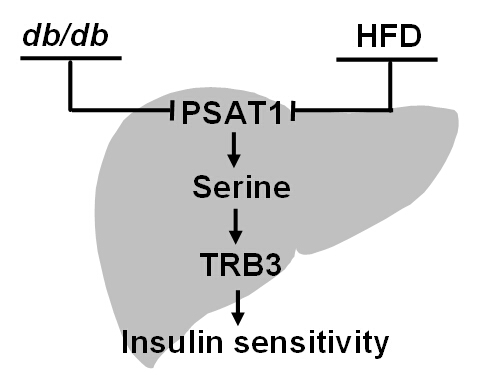
PSAT1 regulates insulin sensitivity through serine-TRB3 pathway (Image by Dr. GUO Feifan’s group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

