
Phononic crystals (PCs) consisting of periodic elastic materials have a property of band gaps which have potential applications such as acoustic filter, waveguides and acoustic resonator. However, most of the prior research of PCs were limited to large and hand-assembled structures at frequencies below 1MHz.
For applying PCs to micro-electro-mechanical systems, band gaps of micromachined air/silicon PCs at hundreds MHZ and GHz for surface acoustic waves (SAW) were theoretically and experimentally demonstrated before. It showed potential to SAW devices such as high-Q resonant cavity. After that, a novel type of micro piezoelectric PCs with aluminum (Al) stubs on 128º-YXLiNbO3 substrate combined with SAW devices was studied using 2-dimensional finite difference time domain(2-D FDTD) model. However, it took hypothetic exciting source and didn’t consider the mechanical loading effect of finite-thickness stubs.
In order to analyze the propagation of SAW in the Al/128º-YXLiNbO3 PCs accurately, recently, researchers provide a 3-dimensional (3-D) model by using the finite element method (FEM). With the FEM, two 3-D models of SAW delay lines are built respectively with and without Al/128º-YXLiNbO3 PCs.
Interdigital transducers are used to excite Rayleigh SAW exactly, while the hypothetic exciting source is used in 2-D FDTD model. With comparing their received signal, transmission of PCs can be obtained. And perfect matching layer is used to absorb the reflective waves in direction of wave propagation. Besides, to reduce the time and memory cost of 3-D model, period boundary condition is adopted in direction perpendicular to the wave propagation.
Experiments are designed to measure the band gaps of PCs with network analyzer. Fig.1 displays the displacement field distribution using 3-D FEM model. It shows exactly the Rayleigh SAW propagating as acoustic field are mainly displacements of Ux and Uz focusing on the surface. It demonstrates the reliability of the model used to analyze Rayleigh SAW propagation. Fig.2 shows the transmission results of 2-D FDTD, 3-D FEM and experiments respectively, where the 3-D FEM model denotes higher accuracy than 2-D FDTD in the passband due to considering the mechanical loading effect of finite-thickness stubs.
This model has proved to be accurate to analyze Rayleigh SAW propagation in the piezoelectric PCs and can be extended to analyze more properties of Rayleigh SAW devices based on PCs.
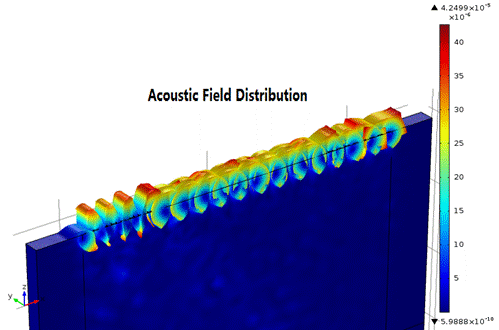
Fig.1 Acoustic field distribution (Image by LI).
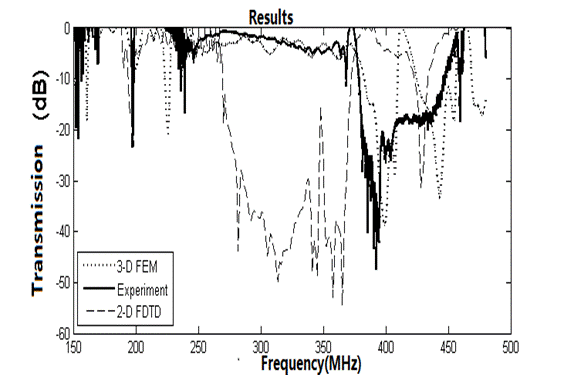
Fig.2 Transmission results of experiments and theory (Image by LI).
References:
LI Honglang, TIAN Yahui, KE Yabing, LUO Wei, HE Shitang. Analysis of Rayleigh Surface Acoustic Waves Propagation on Piezoelectric Phononic Crystal with 3-D Finite Element Model. 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings (pp. 2533-2536, September 2014, Chicago, IL). DOI: 10.1109/ULTSYM.2014.0632
Contact:
TIAN Yahui
Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 100190 Beijing, China
E-mail: tianyahui@mail.ioa.ac.cn or yahuitian@yeah.net

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

